A CPF-like phosphatase module links transcription termination to chromatin silencing
- PMID: 38851185
- PMCID: PMC7616277
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2024.05.016
A CPF-like phosphatase module links transcription termination to chromatin silencing
Abstract
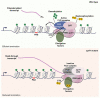
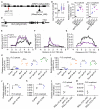
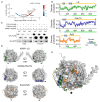
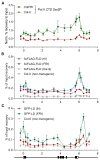
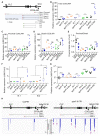
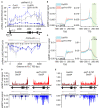
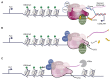
The interconnections between co-transcriptional regulation, chromatin environment, and transcriptional output remain poorly understood. Here, we investigate the mechanism underlying RNA 3' processing-mediated Polycomb silencing of Arabidopsis FLOWERING LOCUS C (FLC). We show a requirement for ANTHESIS PROMOTING FACTOR 1 (APRF1), a homolog of yeast Swd2 and human WDR82, known to regulate RNA polymerase II (RNA Pol II) during transcription termination. APRF1 interacts with TYPE ONE SERINE/THREONINE PROTEIN PHOSPHATASE 4 (TOPP4) (yeast Glc7/human PP1) and LUMINIDEPENDENS (LD), the latter showing structural features found in Ref2/PNUTS, all components of the yeast and human phosphatase module of the CPF 3' end-processing machinery. LD has been shown to co-associate in vivo with the histone H3 K4 demethylase FLOWERING LOCUS D (FLD). This work shows how the APRF1/LD-mediated polyadenylation/termination process influences subsequent rounds of transcription by changing the local chromatin environment at FLC.
Keywords: COOLAIR; ChIP; FLC; IP-MS; Quant-seq; RNA 3′ processing; chromatin silencing; co-transcriptional processing; plaNET-seq; transcription termination.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests L.A.P. is on the advisory board for Molecular Cell.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

