Defects in B-lymphopoiesis and B-cell maturation underlie prolonged B-cell depletion in ANCA-associated vasculitis
- PMID: 38851295
- PMCID: PMC11503191
- DOI: 10.1136/ard-2024-225587
Defects in B-lymphopoiesis and B-cell maturation underlie prolonged B-cell depletion in ANCA-associated vasculitis
Abstract
Objectives: B-cell depletion time after rituximab (RTX) treatment is prolonged in antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody (ANCA)-associated vasculitis (AAV) compared with other autoimmune diseases. We investigated central and peripheral B-cell development to identify the causes for the defect in B-cell reconstitution after RTX therapy.
Methods: We recruited 91 patients with AAV and performed deep phenotyping of the peripheral and bone marrow B-cell compartment by spectral flow and mass cytometry. B-cell development was studied by in vitro modelling and the role of BAFF receptor by quantitative PCR, western blot analysis and in vitro assays.
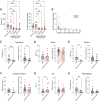
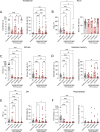
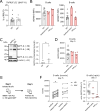
Results: Treatment-naïve patients with AAV showed low transitional B-cell numbers, suggesting impaired B-lymphopoiesis. We analysed bone marrow of treatment-naïve and RTX-treated patients with AAV and found reduced B-lymphoid precursors. In vitro modelling of B-lymphopoiesis from AAV haematopoietic stem cells showed intact, but slower and reduced immature B-cell development. In a subgroup of patients, after RTX treatment, the presence of transitional B cells did not translate in replenishment of naïve B cells, suggesting an impairment in peripheral B-cell maturation. We found low BAFF-receptor expression on B cells of RTX-treated patients with AAV, resulting in reduced survival in response to BAFF in vitro.
Conclusions: Prolonged depletion of B cells in patients with AAV after RTX therapy indicates a B-cell defect that is unmasked by RTX treatment. Our data indicate that impaired bone marrow B-lymphopoiesis results in a delayed recovery of peripheral B cells that may be further aggravated by a survival defect of B cells. Our findings contribute to the understanding of AAV pathogenesis and may have clinical implications regarding RTX retreatment schedules and immunomonitoring after RTX therapy.
Keywords: B-lymphocytes; rituximab; vasculitis.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2024. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ on behalf of EULAR.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Highly Sensitive Flow Cytometric Detection of Residual B-Cells After Rituximab in Anti-Neutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibodies-Associated Vasculitis Patients.Front Immunol. 2020 Dec 15;11:566732. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.566732. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 33384685 Free PMC article.
-
B cell repopulation kinetics after rituximab treatment in ANCA-associated vasculitides compared to rheumatoid arthritis, and connective tissue diseases: a longitudinal observational study on 120 patients.Arthritis Res Ther. 2017 May 18;19(1):101. doi: 10.1186/s13075-017-1306-0. Arthritis Res Ther. 2017. PMID: 28521808 Free PMC article.
-
Reconstitution of the peripheral B lymphocyte compartment in patients with ANCA-associated vasculitides treated with rituximab for relapsing or refractory disease.Autoimmunity. 2014 Sep;47(6):401-8. doi: 10.3109/08916934.2014.914174. Epub 2014 May 6. Autoimmunity. 2014. PMID: 24798501
-
B-cell-targeted therapy in systemic vasculitis.Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2016 Jan;28(1):15-20. doi: 10.1097/BOR.0000000000000235. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2016. PMID: 26599379 Review.
-
Is B-cell depletion first choice in antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis?Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2014 May;26(3):292-8. doi: 10.1097/BOR.0000000000000049. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2014. PMID: 24646946 Review.
Cited by
-
Modulating IL-21-driven B cell responses in idiopathic inflammatory myopathies via inhibition of the JAK/STAT pathway.Arthritis Res Ther. 2025 Apr 1;27(1):76. doi: 10.1186/s13075-025-03547-2. Arthritis Res Ther. 2025. PMID: 40170058 Free PMC article.
-
Persistent B Cell Depletion After Rituximab for Autoimmune and Glomerular Diseases: A Case Series.Kidney Int Rep. 2025 Feb 7;10(5):1441-1449. doi: 10.1016/j.ekir.2025.02.002. eCollection 2025 May. Kidney Int Rep. 2025. PMID: 40485690 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in the treatment of ANCA-associated vasculitis.Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2025 Jul;21(7):396-413. doi: 10.1038/s41584-025-01266-1. Epub 2025 Jun 5. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2025. PMID: 40473820 Review.
-
Aging in Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis and Microscopic Polyangiitis: From Pathophysiology to Clinical Management.Drugs Aging. 2025 Jul;42(7):615-631. doi: 10.1007/s40266-025-01210-8. Epub 2025 May 31. Drugs Aging. 2025. PMID: 40448791 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Senescence, NK cells, and cancer: navigating the crossroads of aging and disease.Front Immunol. 2025 Apr 4;16:1565278. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1565278. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40255394 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

