Novel FFPE proteomics method suggests prolactin induced protein as hormone induced cytoskeleton remodeling spatial biomarker
- PMID: 38851810
- PMCID: PMC11162451
- DOI: 10.1038/s42003-024-06354-8
Novel FFPE proteomics method suggests prolactin induced protein as hormone induced cytoskeleton remodeling spatial biomarker
Abstract
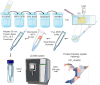
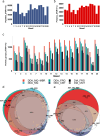
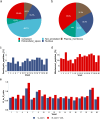
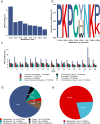
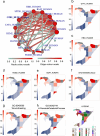
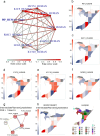
Robotically assisted proteomics provides insights into the regulation of multiple proteins achieving excellent spatial resolution. However, developing an effective method for spatially resolved quantitative proteomics of formalin fixed paraffin embedded tissue (FFPE) in an accessible and economical manner remains challenging. We introduce non-robotic In-insert FFPE proteomics approach, combining glass insert FFPE tissue processing with spatial quantitative data-independent mass spectrometry (DIA). In-insert approach identifies 450 proteins from a 5 µm thick breast FFPE tissue voxel with 50 µm lateral dimensions covering several tens of cells. Furthermore, In-insert approach associated a keratin series and moesin (MOES) with prolactin-induced protein (PIP) indicating their prolactin and/or estrogen regulation. Our data suggest that PIP is a spatial biomarker for hormonally triggered cytoskeletal remodeling, potentially useful for screening hormonally affected hotspots in breast tissue. In-insert proteomics represents an alternative FFPE processing method, requiring minimal laboratory equipment and skills to generate spatial proteotype repositories from FFPE tissue.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
In-Depth Mass Spectrometry-Based Proteomics of Formalin-Fixed, Paraffin-Embedded Tissues with a Spatial Resolution of 50-200 μm.J Proteome Res. 2022 Sep 2;21(9):2237-2245. doi: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.2c00409. Epub 2022 Aug 2. J Proteome Res. 2022. PMID: 35916235 Free PMC article.
-
Equivalence of protein inventories obtained from formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded and frozen tissue in multidimensional liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry shotgun proteomic analysis.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2009 Aug;8(8):1988-98. doi: 10.1074/mcp.M800518-MCP200. Epub 2009 May 24. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2009. PMID: 19467989 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Proteomics for Meningioma: An Integrated Workflow for Quantitative Proteomics and Biomarker Validation in Formalin-Fixed Paraffin-Embedded Tissue Samples.OMICS. 2022 Sep;26(9):512-520. doi: 10.1089/omi.2022.0082. Epub 2022 Aug 26. OMICS. 2022. PMID: 36036964
-
Making Formalin-Fixed, Paraffin Embedded Blocks.Methods Mol Biol. 2019;1897:253-268. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-8935-5_22. Methods Mol Biol. 2019. PMID: 30539450 Review.
-
Biomedical analysis of formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissue samples: The Holy Grail for molecular diagnostics.J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2018 Jun 5;155:125-134. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2018.03.065. Epub 2018 Apr 2. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2018. PMID: 29627729 Review.
Cited by
-
DIA/SWATH-Mass Spectrometry Revealing Melanoma Cell Proteome Transformations with Silver Nanoparticles: An Innovative Comparative Study.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Feb 26;26(5):2029. doi: 10.3390/ijms26052029. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40076651 Free PMC article.
-
Spatial omics technology potentially promotes the progress of tumor immunotherapy.Br J Cancer. 2025 Sep;133(4):421-434. doi: 10.1038/s41416-025-03075-5. Epub 2025 Jun 2. Br J Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40456924 Review.
-
Application of Spatial Omics in the Cardiovascular System.Research (Wash D C). 2025 Mar 8;8:0628. doi: 10.34133/research.0628. eCollection 2025. Research (Wash D C). 2025. PMID: 40062231 Free PMC article. Review.
-
High-throughput proteomic and phosphoproteomic analysis of formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissue.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Dec 7:2024.11.17.624038. doi: 10.1101/2024.11.17.624038. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Mol Cell Proteomics. 2025 Jul 29:101044. doi: 10.1016/j.mcpro.2025.101044. PMID: 39605438 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
A graph self-supervised residual learning framework for domain identification and data integration of spatial transcriptomics.Commun Biol. 2024 Sep 12;7(1):1123. doi: 10.1038/s42003-024-06814-1. Commun Biol. 2024. PMID: 39266614 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

