Dual inhibition of the TrkA and JAK2 pathways using entrectinib and pacritinib suppresses the growth and metastasis of HER2-positive and triple-negative breast cancers
- PMID: 38852701
- PMCID: PMC11533721
- DOI: 10.1016/j.canlet.2024.217023
Dual inhibition of the TrkA and JAK2 pathways using entrectinib and pacritinib suppresses the growth and metastasis of HER2-positive and triple-negative breast cancers
Abstract
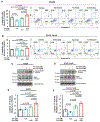
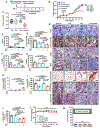
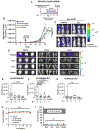
HER2-positive and triple-negative breast cancers (TNBC) are difficult to treat and associated with poor prognosis. Despite showing initial response, HER2-positive breast cancers often acquire resistance to HER2-targeted therapies, and TNBC lack effective therapies. To overcome these clinical challenges, we evaluated the therapeutic utility of co-targeting TrkA and JAK2/STAT3 pathways in these breast cancer subtypes. Here, we report the novel combination of FDA-approved TrkA inhibitors (Entrectinib or Larotrectinib) and JAK2 inhibitors (Pacritinib or Ruxolitinib) synergistically inhibited in vitro growth of HER2-positive breast cancer cells and TNBC cells. The Entrectinib-Pacritinib combination inhibited the breast cancer stem cell subpopulation, reduced expression of stemness genes, SOX2 and MYC, and induced apoptosis. The Entrectinib-Pacritinib combination suppressed orthotopic growth of HER2-positive Trastuzumab-refractory breast cancer xenografts and basal patient-derived xenograft (PDXs), reduced tumoral SOX2 and MYC, and induced apoptosis in both mouse models. The Entrectinib-Pacritinib combination inhibited overall metastatic burden, and brain and bone metastases of intracardially inoculated TNBC cells without toxicity. Together, our results demonstrate for the first time that co-inhibition of TrkA and JAK2 synergistically suppresses breast cancer growth and metastasis, thereby providing preclinical evidence that supports future clinical evaluations.
Keywords: Breast cancer; Breast cancer metastasis; Combined targeted therapy; JAK2; TrkA.
Copyright © 2024 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures



References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fuchs HE, Jemal A, Cancer statistics, CA A Cancer J. Clin 72 (2022) 7–33, 2022. - PubMed
-
- Howlader N, Noone AM, Krapcho M, Miller D, Brest A, Yu M, et al. SEER Cancer Statistics Review, 1975-2016, National Cancer Institute. Bethesda, MD, https://seer.cancer.gov/csr/1975_2016/, based on November 2018 SEER data submission, posted to the SEER web site, April 2019.
-
- Perou CM, Sorlie T, Eisen MB, van de Rijn M, Jeffrey SS, Rees CA, et al., Molecular portraits of human breast tumours, Nature 406 (2000) 747–752. - PubMed
-
- Waks AG, Winer EP, Breast cancer treatment: a review, JAMA 321 (2019) 288–300. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

