Estimated Doses to the Heart, Lungs and Oesophagus and Risks From Typical UK Radiotherapy for Early Breast Cancer During 2015-2023
- PMID: 38853062
- PMCID: PMC11511668
- DOI: 10.1016/j.clon.2024.05.002
Estimated Doses to the Heart, Lungs and Oesophagus and Risks From Typical UK Radiotherapy for Early Breast Cancer During 2015-2023
Abstract
Purpose: Breast cancer radiotherapy can increase the risks of heart disease, lung cancer and oesophageal cancer. At present, the best dosimetric predictors of these risks are mean doses to the whole heart, lungs and oesophagus, respectively. We aimed to estimate typical doses to these organs and resulting risks from UK breast cancer radiotherapy.
Methods: A systematic review and meta-analysis was conducted of planned or delivered mean doses to the whole heart, lungs or oesophagus from UK breast cancer radiotherapy in studies published during 2015-2023. Average mean doses were summarised for combinations of laterality and clinical targets. Heart disease and lung cancer mortality risks were then estimated using established models.
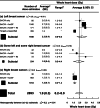
Results: For whole heart, thirteen studies reported 2893 doses. Average mean doses were higher in left than in right-sided radiotherapy and increased with extent of clinical targets. For left-sided radiotherapy, average mean heart doses were: 2.0 Gy (range 1.2-8.0 Gy) breast/chest wall, 2.7 Gy (range 0.6-5.6 Gy) breast/chest wall with either axilla or supraclavicular nodes and 2.9 Gy (range 1.3-4.7 Gy) breast/chest wall with nodes including internal mammary. For right-sided radiotherapy, average mean heart doses were: 1.0 Gy (range 0.3-1.0 Gy) breast/chest wall and 1.2 Gy (range 1.0-1.4 Gy) breast/chest wall with either axilla or supraclavicular nodes. There were no whole heart dose estimates from right internal mammary radiotherapy. For whole lung, six studies reported 2230 doses. Average mean lung doses increased with extent of targets irradiated: 2.6 Gy (range 1.4-3.0 Gy) breast/chest wall, 3.0 Gy (range 0.9-5.1 Gy) breast/chest wall with either axilla or supraclavicular nodes and 7.1 Gy (range 6.7-10.0 Gy) breast/chest wall with nodes including internal mammary. For whole oesophagus, two studies reported 76 doses. Average mean oesophagus doses increased with extent of targets irradiated: 1.4 Gy (range 1.0-2.0 Gy) breast/chest wall with either axilla or supraclavicular nodes and 5.8 Gy (range 1.9-10.0 Gy) breast/chest wall with nodes including internal mammary.
Conclusions: The typical doses to these organs may be combined with dose-response relationships to estimate radiation risks. Estimated 30-year absolute lung cancer mortality risks from modern UK breast cancer radiotherapy for patients irradiated when aged 50 years were 2-6% for long-term continuing smokers, and <1% for non-smokers. Estimated 30-year mortality risks for heart disease were <1%.
Keywords: Breast cancer radiotherapy; Heart dose; Lung dose; Oesophagus dose; Radiotherapy risks; UK radiotherapy.
Copyright © 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Cancer Research UK Breast Cancer Statistics. 2023 https://www.cancerresearchuk.org/health-professional/cancer-statistics/s...
-
- Early Breast Cancer Trialists’ Collaborative Group Effect of radiotherapy after breast-conserving surgery on 10-year recurrence and 15-year breast cancer death: meta-analysis of individual patient data for 10,801 women in 17 randomised trials. Lancet. 2011;378(9804):1707–1716. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(11)61629-2. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Early Breast Cancer Trialists’ Collaborative Group Effect of radiotherapy after mastectomy and axillary surgery on 10-year recurrence and 20-year breast cancer mortality: meta-analysis of individual patient data for 8135 women in 22 randomised trials. Lancet. 2014;383(9935):2127–2135. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(14)60488-8. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

