Lab-on-a-chip: an advanced technology for the modernization of traditional Chinese medicine
- PMID: 38853247
- PMCID: PMC11163804
- DOI: 10.1186/s13020-024-00956-4
Lab-on-a-chip: an advanced technology for the modernization of traditional Chinese medicine
Abstract
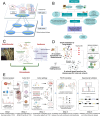
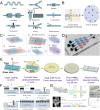
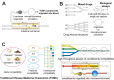
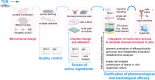
Benefiting from the complex system composed of various constituents, medicament portions, species, and places of origin, traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) possesses numerous customizable and adaptable efficacies in clinical practice guided by its theories. However, these unique features are also present challenges in areas such as quality control, screening active ingredients, studying cell and organ pharmacology, and characterizing the compatibility between different Chinese medicines. Drawing inspiration from the holistic concept, an integrated strategy and pattern more aligned with TCM research emerges, necessitating the integration of novel technology into TCM modernization. The microfluidic chip serves as a powerful platform for integrating technologies in chemistry, biology, and biophysics. Microfluidics has given rise to innovative patterns like lab-on-a-chip and organoids-on-a-chip, effectively challenging the conventional research paradigms of TCM. This review provides a systematic summary of the nature and advanced utilization of microfluidic chips in TCM, focusing on quality control, active ingredient screening/separation, pharmaceutical analysis, and pharmacological/toxicological assays. Drawing on these remarkable references, the challenges, opportunities, and future trends of microfluidic chips in TCM are also comprehensively discussed, providing valuable insights into the development of TCM.
Keywords: Active ingredient screening; Compatibility of traditional Chinese medicine; Microfluidic chip; Pharm-lab-on-a-chip; Quality control; Traditional Chinese medicine.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Luo G, Liang Q, Wang Y. Fingerprinting of Chinese materia medica: quality evaluation. Ltd: Quality Control and New Drug Development. Chemical Industry Press Co.; 2009. pp. 1–20.
-
- Luo G, Wang Y, Liang Q, Liu Q. Systems biology for traditional Chinese medicine. Hoboken: Wiley; 2012. pp. 1–33.
-
- Li S. Network pharmacology evaluation method guidance - draft. World J Tradit Chin Med. 2021;7(1):146–154. doi: 10.4103/wjtcm.wjtcm_11_21. - DOI
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

