A morphological analysis of calcium hydroxylapatite and poly-l-lactic acid biostimulator particles
- PMID: 38853456
- PMCID: PMC11163027
- DOI: 10.1111/srt.13764
A morphological analysis of calcium hydroxylapatite and poly-l-lactic acid biostimulator particles
Abstract
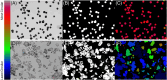
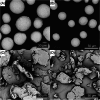
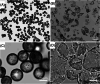
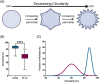
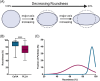
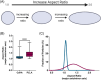
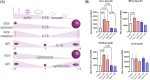
Injectable fillers, pivotal in aesthetic medicine, have evolved significantly with recent trends favoring biostimulators like calcium hydroxylapatite (CaHA-CMC; Radiesse, Merz Aesthetics, Raleigh, NC) and poly-l-lactic acid (PLLA; Sculptra Aesthetics, Galderma, Dallas, TX). This study aims to compare the particle morphology of these two injectables and examine its potential clinical implications. Utilizing advanced light and scanning electron microscopy techniques, the physical characteristics of CaHA-CMC and PLLA particles were analyzed, including shape, size, circularity, roundness, aspect ratio, and quantity of phagocytosable particles. The findings reveal several morphological contrasts: CaHA-CMC particles exhibited a smooth, homogenous, spherical morphology with diameters predominantly ranging between 20 and 45 µm, while PLLA particles varied considerably in shape and size, appearing as micro flakes ranging from 2 to 150 µm in major axis length. The circularity and roundness of CaHA-CMC particles were significantly higher compared to PLLA, indicating a more uniform shape. Aspect ratio analysis further underscored these differences, with CaHA-CMC particles showing a closer resemblance to circles, unlike the more oblong PLLA particles. Quantification of the phagocytosable content of both injectables revealed a higher percentage of phagocytosable particles in PLLA. These morphological distinctions may influence the tissue response to each treatment. CaHA-CMC's uniform, spherical particles may result in reduced inflammatory cell recruitment, whereas PLLA's heterogeneous particle morphology may evoke a more pronounced inflammatory response.
Keywords: CaHA; PLLA; calcium hydroxylapatite; poly‐l‐lactic acid; radiesse; sculptra.
© 2024 The Author(s). Skin Research and Technology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
McCarthy and Hartmann are employed by Merz Aesthetics. Shahriar and Xie have no conflicts to disclose. Durkin is a paid consultant, speaker, and trainer for Merz Aesthetics, Suneva, Apyx Medical,Babor, GloPharma, Alastin, Allergan, and the MusculoSkeletan Transplant Foundation. Khalifian is a paid consultant, speaker, trainer, and researcher for Allergan Aesthetics, Benev, Sciton, and Merz Aesthetics.
Figures

References
-
- Tijerina JD, Morrison SD, Nolan IT, Parham MJ, Nazerali R. Predicting public interest in nonsurgical cosmetic procedures using google trends. Aesthet Surg J. 2020;40:1253–1262. - PubMed
-
- Haddad S, Galadari H, Patil A, Goldust M, Al Salam S, Guida S. Evaluation of the biostimulatory effects and the level of neocollagenesis of dermal fillers: a review. Int J Dermatol. 2022;61(10):1284‐1288. - PubMed
-
- Nowag B, Casabona G, Kippenberger S, Zöller N, Hengl T. Calcium hydroxylapatite microspheres activate fibroblasts through direct contact to stimulate neocollagenesis. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2022;22(2):426‐432. - PubMed
-
- Courderot‐Masuyer C, Robin S, Tauzin H, Humbert P. Evaluation of lifting and antiwrinkle effects of calcium hydroxylapatite filler. In vitro quantification of contractile forces of human wrinkle and normal aged fibroblasts treated with calcium hydroxylapatite. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2016;15:260–268. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

