Activity-dependent diffusion trapping of AMPA receptors as a key step for expression of early LTP
- PMID: 38853553
- PMCID: PMC11343219
- DOI: 10.1098/rstb.2023.0220
Activity-dependent diffusion trapping of AMPA receptors as a key step for expression of early LTP
Abstract
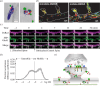
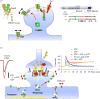
This review focuses on the activity-dependent diffusion trapping of α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid receptors (AMPARs) as a crucial mechanism for the expression of early long-term potentiation (LTP), a process central to learning and memory. Despite decades of research, the precise mechanisms by which LTP induction leads to an increase in AMPAR responses at synapses have been elusive. We review the different hypotheses that have been put forward to explain the increased AMPAR responsiveness during LTP. We discuss the dynamic nature of AMPAR complexes, including their constant turnover and activity-dependent modifications that affect their synaptic accumulation. We highlight a hypothesis suggesting that AMPARs are diffusively trapped at synapses through activity-dependent interactions with protein-based binding slots in the post-synaptic density (PSD), offering a potential explanation for the increased synaptic strength during LTP. Furthermore, we outline the challenges still to be addressed before we fully understand the functional roles and molecular mechanisms of AMPAR dynamic nanoscale organization in LTP. This article is part of a discussion meeting issue 'Long-term potentiation: 50 years on'.
Keywords: AMPAR diffusion trapping; AMPAR trafficking; long-term potentiation; synaptic plasticity.
Conflict of interest statement
We declare we have no competing interests.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
