Safety and Immunogenicity of a 4-Component Generalized Modules for Membrane Antigens Shigella Vaccine in Healthy European Adults: Randomized, Phase 1/2 Study
- PMID: 38853614
- PMCID: PMC11481318
- DOI: 10.1093/infdis/jiae273
Safety and Immunogenicity of a 4-Component Generalized Modules for Membrane Antigens Shigella Vaccine in Healthy European Adults: Randomized, Phase 1/2 Study
Erratum in
-
Correction to: Safety and Immunogenicity of a 4-Component Generalized Modules for Membrane Antigens Shigella Vaccine in Healthy European Adults: Randomized, Phase 1/2 Study.J Infect Dis. 2024 Dec 16;230(6):e1413. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiae564. J Infect Dis. 2024. PMID: 39566030 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: We report data from stage 1 of an ongoing 2-staged, phase 1/2 randomized clinical trial with a 4-component generalized modules for membrane antigens-based vaccine against Shigella sonnei and Shigella flexneri 1b, 2a, and 3a (altSonflex1-2-3; GSK).
Methods: Europeans aged 18-50 years (N = 102) were randomized (2:1) to receive 2 injections of altSonflex1-2-3 or placebo at 3- or 6-month interval. Safety and immunogenicity were assessed at prespecified time points.
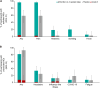
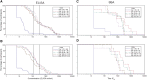
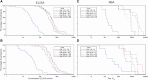
Results: The most common solicited administration-site event (until 7 days after each injection) and unsolicited adverse event (until 28 days after each injection) were pain (altSonflex1-2-3, 97.1%; placebo, 58.8%) and headache (32.4%; 23.5%), respectively. All serotype-specific functional IgG antibodies peaked 14-28 days after injection 1 and remained substantially higher than prevaccination at 3 or 6 months postvaccination; the second injection did not boost but restored the initial immune response. The highest seroresponse rates (≥4-fold increase in titers over baseline) were obtained against S. flexneri 2a (enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay [ELISA] after injection 1, 91.0%; after injection 2 [day 113; day 197], 100%; 97.0% and serum bactericidal activity [SBA] after injection 1, 94.4%; after injection 2, 85.7%; 88.9%) followed by S. sonnei (ELISA after injection 1, 77.6%; after injection 2, 84.6%; 78.8% and SBA after injection 1, 83.3%; after injection 2, 71.4%; 88.9%). Immune responses against S. flexneri 1b and S. flexneri 3a, as measured by both ELISA and SBA, were numerically lower compared to those against S. sonnei and S. flexneri 2a.
Conclusions: No safety signals or concerns were identified. altSonflex1-2-3 induced functional serotype-specific immune responses, allowing further clinical development in the target population. Clinical Trials Registration . NCT05073003.
Keywords: Shigella vaccine; O-antigen; altSonflex1-2-3; immunogenicity; safety.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Infectious Diseases Society of America.
Conflict of interest statement
Potential conflicts of interest. U. N. N., F. Ma., E. S., J. J., G. L. C., A. S. B., C. G. V., P. F., E. M., F. N., R. R., I. D. R., J. A., A. M. C., F. B. S., O. R., V. C., F. Mi., A. K. A., and A. P. are or were employees of GSK when the study was designed, initiated, and/or conducted. U. N. N., J. J., G. L. C., A. S. B., C. G. V., F. N., I. D. R., J. A., F. B. S., O. R., V. C., F. Mi., A. K. A., and A. P. hold shares in GSK as part of their remuneration. A. K. A. reports GSK scientific writer support for this study. F. Mi. reports a patent issued on the 4-component Shigella GMMA formulation. I. L. R. reports funding to her institution for the conduct of GSK Vaccines Institute for Global Health (GVGH) studies; being a data safety monitoring board member of a phase 3 (non-Shigella) vaccine trial for Janssen Vaccines; and funding to her institution for the conduct of various vaccine trials (none were Shigella vaccine studies) from GSK, Janssen, Curevac, Osivax, Vaccitech, Icosavax, OSE Immunotherapeutics, Icon Genetics, Virometix, and MSD. All other authors report no potential conflicts. All authors have submitted the ICMJE Form for Disclosure of Potential Conflicts of Interest. Conflicts that the editors consider relevant to the content of the manuscript have been disclosed.
Figures

References
-
- Hale TL, Keusch GT. Shigella. In: Baron S, ed. Medical microbiology. 4th ed. Galveston, TX: University of Texas Medical Branch at Galveston, 1996. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK8038/. - PubMed
-
- Percival SL, Williams DW. Shigella. In: Percival SL, Yates MV, Williams DW, Chalmers RM, Gray NF, eds. Microbiology of waterborne diseases. 2nd ed. London: Academic Press, 2014:223–36. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9780124158467000111.
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention . Shigellosis. CDC Yellow Book 2024. 2023. https://wwwnc.cdc.gov/travel/yellowbook/2024/infections-diseases/shigell.... Accessed 21 November 2023.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

