A model for competency-based training of undergraduate medical students to perform screening and brief intervention in alcohol use disorder-Findings from a study in a medical college in Delhi
- PMID: 38853801
- PMCID: PMC11155660
- DOI: 10.4103/ipj.ipj_35_23
A model for competency-based training of undergraduate medical students to perform screening and brief intervention in alcohol use disorder-Findings from a study in a medical college in Delhi
Abstract
Background: Alcohol use disorder (AUD) is a major cause of prolonged disability and an economic burden on communities across the world. The undergraduate (UG) curriculum in medical school in India does not allow adequate time to a structured learning about alcohol use disorder, its treatment, and prevention. The screening and brief intervention module (SBI) developed by the World Health Organisation (WHO) is an effective way to reduce drinking among risky drinkers. Training of undergraduates in SBI may go a long way in early intervention among problem drinkers. Hence, there is a felt need to incorporated the module in the clinical training schedule to enhance SBI skills among UGs to provide appropriate intervention at the primary healthcare level.
Methodology: 50 final year UG students of a medical college in Delhi were exposed to a competency-based training in alcohol SBI comprised of lectures, focused group discussions (FGD), and role-play during their 2-week clinical posting in psychiatry along with a hands-on training under supervision of faculty. Subsequently, they were assessed for knowledge and skills gained through objective-structured clinical examination (OSCE) and feedback taken from students about changes in their knowledge and attitudes towards alcohol use disorder SBI.
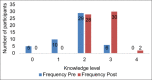
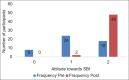
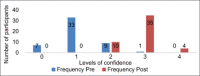
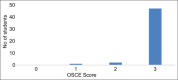
Results: Pre- and post-self-reported outcome variables revealed significant positive impact (p < 0.001) of SBI module on competency of students in implementing SBI on patients. Assessment of knowledge on OSCE revealed mean scores of 9.48 ± 1.20 on 10 MCQs (of 01 mark each) with 47 students scoring 80% or above. On integrated OSCE assessment of competencies, 94% students made satisfactory demonstration at a desired level. Attendance in lectures and supervised SBI, attitudes pre- and post-intervention and confidence level post-intervention were found to be predictors of a high MCQ score. All faculty agreed about the feasibility of implementing competency-based SBI in existing clinical posting schedule.
Conclusion: The study has demonstrated the feasibility of teaching competency-based alcohol SBI to undergraduate medical students in existing clinical posting curriculum in psychiatry and its efficacy in having a positive impact on the perception and approach of the students towards patients with alcohol use disorder.
Keywords: Alcohol use disorder; screening and brief intervention; undergraduate medical students.
Copyright: © 2023 Industrial Psychiatry Journal.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A Web-Based Alcohol Screening and Brief Intervention Training Module Within Physician Assistant Programs in the Midwest to Increase Knowledge, Attitudes, and Confidence: Evaluation Study.JMIR Ment Health. 2019 Oct 23;6(10):e11963. doi: 10.2196/11963. JMIR Ment Health. 2019. PMID: 31647473 Free PMC article.
-
Rheumatology training and awareness among undergraduates in Indian medical schools: a multicenter observational study.BMC Med Educ. 2025 Mar 9;25(1):355. doi: 10.1186/s12909-025-06843-2. BMC Med Educ. 2025. PMID: 40059150 Free PMC article.
-
Development and implementation of a competency-based module for teaching research methodology to medical undergraduates.J Educ Health Promot. 2019 Aug 30;8:164. doi: 10.4103/jehp.jehp_133_19. eCollection 2019. J Educ Health Promot. 2019. PMID: 31544129 Free PMC article.
-
Psychiatry training for medical students: A global perspective and implications for India's competency-based medical education curriculum.Indian J Psychiatry. 2022 May-Jun;64(3):240-251. doi: 10.4103/indianjpsychiatry.indianjpsychiatry_187_22. Epub 2022 Jun 8. Indian J Psychiatry. 2022. PMID: 35859553 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Strengthening clinical microbiology skill acquisition; a nationwide survey of faculty perceptions & practices on teaching & assessment of practical skills to undergraduate students.Indian J Med Microbiol. 2021 Apr;39(2):154-158. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmmb.2020.11.003. Epub 2020 Dec 9. Indian J Med Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33966857 Review.
References
-
- WHO factsheet: Alcohol. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/alcohol. [Last accessed on 2022 May 05]
-
- Ministry of Social Justice & Empowerment National survey report-Magnitude of Substance use in India. 2019 Feb;
-
- World Health Organization Publication; 2003. Screening and brief intervention.
-
- Burden and Socio-Economic Impact of alcohol -The Bangalore Study by WHO South East Asia Region. 2006
-
- World Health Organization; 2017. WHO alcohol brief intervention training manual for primary care.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources