This is a preprint.
Role of the CTCF Binding Site in Human T-Cell Leukemia Virus-1 Pathogenesis
- PMID: 38853836
- PMCID: PMC11160593
- DOI: 10.1101/2024.05.28.596170
Role of the CTCF Binding Site in Human T-Cell Leukemia Virus-1 Pathogenesis
Update in
-
Role of the CTCF binding site in Human T-Cell Leukemia Virus-1 pathogenesis.PLoS Pathog. 2025 Jun 3;21(6):e1012293. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1012293. eCollection 2025 Jun. PLoS Pathog. 2025. PMID: 40460345 Free PMC article.
Abstract
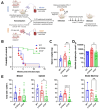
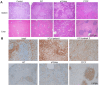
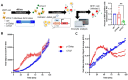
During HTLV-1 infection, the virus integrates into the host cell genome as a provirus with a single CCCTC binding protein (CTCF) binding site (vCTCF-BS), which acts as an insulator between transcriptionally active and inactive regions. Previous studies have shown that the vCTCF-BS is important for maintenance of chromatin structure, regulation of viral expression, and DNA and histone methylation. Here, we show that the vCTCF-BS also regulates viral infection and pathogenesis in vivo in a humanized (Hu) mouse model of adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma. Three cell lines were used to initiate infection of the Hu-mice, i) HTLV-1-WT which carries an intact HTLV-1 provirus genome, ii) HTLV-1-CTCF, which contains a provirus with a mutated vCTCF-BS which abolishes CTCF binding, and a stop codon immediate upstream of the mutated vCTCF-BS which deletes the last 23 amino acids of p12, and iii) HTLV-1-p12stop that contains the intact vCTCF-BS, but retains the same stop codon in p12 as in the HTLV-1-CTCF cell line. Hu-mice were infected with mitomycin treated or irradiated HTLV-1 producing cell lines. There was a delay in pathogenicity when Hu-mice were infected with the CTCF virus compared to mice infected with either p12 stop or WT virus. Proviral load (PVL), spleen weights, and CD4 T cell counts were significantly lower in HTLV-1-CTCF infected mice compared to HTLV-1-p12stop infected mice. Furthermore, we found a direct correlation between the PVL in peripheral blood and death of HTLV-1-CTCF infected mice. In cell lines, we found that the vCTCF-BS regulates Tax expression in a time-dependent manner. The scRNAseq analysis of splenocytes from infected mice suggests that the vCTCF-BS plays an important role in activation and expansion of T lymphocytes in vivo. Overall, these findings indicate that the vCTCF-BS regulates Tax expression, proviral load, and HTLV pathogenicity in vivo.
Keywords: ATL; CTCF; DNA Methylation; Epigenome; HTLV.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Role of the CTCF binding site in Human T-Cell Leukemia Virus-1 pathogenesis.PLoS Pathog. 2025 Jun 3;21(6):e1012293. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1012293. eCollection 2025 Jun. PLoS Pathog. 2025. PMID: 40460345 Free PMC article.
-
HTLV-1 CTCF-binding site is dispensable for in vitro immortalization and persistent infection in vivo.Retrovirology. 2019 Dec 21;16(1):44. doi: 10.1186/s12977-019-0507-9. Retrovirology. 2019. PMID: 31864373 Free PMC article.
-
The retrovirus HTLV-1 inserts an ectopic CTCF-binding site into the human genome.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016 Mar 15;113(11):3054-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1423199113. Epub 2016 Feb 29. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016. PMID: 26929370 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of host immunity on HTLV-1 pathogenesis: potential of Tax-targeted immunotherapy against ATL.Retrovirology. 2019 Aug 22;16(1):23. doi: 10.1186/s12977-019-0484-z. Retrovirology. 2019. PMID: 31438973 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The impact of HTLV-1 on the cellular genome.Curr Opin Virol. 2017 Oct;26:125-131. doi: 10.1016/j.coviro.2017.07.013. Epub 2017 Aug 18. Curr Opin Virol. 2017. PMID: 28822906 Review.
References
-
- Bangham CRM, Matsuoka M. Human T-cell leuekemia virus types 1 and 2. In: Howley PM, Knipe DM, Whelan S, Freed EO, Cohen JL, editors. Fields Virology. RMA Vorises. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2023. p. 527–57.
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
