This is a preprint.
Characterising People who inject drugs, and association with HIV infection: A Situation Analysis in Kampala city, Uganda
- PMID: 38853844
- PMCID: PMC11160897
- DOI: 10.1101/2024.05.31.24308282
Characterising People who inject drugs, and association with HIV infection: A Situation Analysis in Kampala city, Uganda
Update in
-
Characterising people who inject drugs, and association with HIV infection: A situation analysis in Kampala City, Uganda.PLOS Glob Public Health. 2025 Feb 26;5(2):e0003370. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgph.0003370. eCollection 2025. PLOS Glob Public Health. 2025. PMID: 40009634 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Background: Uganda has implemented targeted interventions to address the rising burden of injection drug use, yet barriers persist in reaching persons who inject drugs (PWID). This study describes the characteristics of people who inject drugs, physical and mental health states, and associated risk behaviors, to inform the designing of programs that are tailored to client's needs and preferences.
Methods: A cross-sectional survey was conducted between August and December 2023 at selected hotspots in Kampala, interviewing 499 PWID aged ≥18 years. Data was collected using a semi-structured questionnaire administered by peer educators and Uganda Harm Reduction Network (UHRN) counselors. Measurements included socio-demographics, injecting drug use and sexual risk behaviors, and medical history. HIV serostatus was dtermined by self-report and testing for participants who had no recent history of testing and consented to be tested. Binary logistic regression was used to establish the relationship between HIV infection and risky drug- and sexual behaviors of PWID.
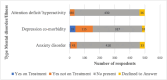
Results: Participants were predominantly Ugandan (95.2%), male (73.2%), unmarried (55.9%), unemployed (81.8%), with higher levels of education and varying ages. Mental disorders were prevalent, with 48.7% reporting at least one underlying condition, including depression (30.8%) and anxiety (9.6%). Physical health issues were also noted, with reported cases of fever (32.9%), cough (32.5%), malaria (22%) and sexually transmitted infections (STIs) (15%).Regarding drug use patterns, the majority (82.6%) were introduced to drugs by close acquaintances, with 70.9% categorized as people who inject drugs. HIV prevalence among injecting drug users was 3.7%, with higher rates among females (8.4%) and non-Ugandans (16.7%). Being female and experiencing difficulty accessing sterile injection materials were associated with HIV-positive status, highlighting the complex interplay between socio-demographic factors, risk behaviors, and HIV infection among individuals with injecting drug use Disorder in Uganda.
Conclusion: Our study provides a comprehensive insight into the socio-demographic, mental, physical health, and HIV risk behavoir of PWID in Kampala, Uganda. The findings indicate significant vulnerabilities to injecting drug use, mental disorders, and high-risk behaviors that predispose this population to HIV infection. Despite a low HIV prevalence compared to previous estimates, the interplay between drug use, risky injecting practices, and sexual behaviors suggests an urgent need for targeted interventions to address these intertwined challenges.
Keywords: HIV; Uganda; harm reduction; injecting drug use; profiles.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- UNODC. World Drug Report (United Nations publication, 2023). 2023.
-
- Degenhardt L, Webb P, Colledge-Frisby S, Ireland J, Wheeler A, Ottaviano S, et al. Epidemiology of injecting drug use, prevalence of injecting-related harm, and exposure to behavioural and environmental risks among people who inject drugs: a systematic review. The Lancet Global Health. 2023. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources