This is a preprint.
Greater inhibition of female rat binge alcohol intake by adrenergic receptor blockers using a novel Two-Shot rat binge drinking model
- PMID: 38853968
- PMCID: PMC11160926
- DOI: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-4402198/v1
Greater inhibition of female rat binge alcohol intake by adrenergic receptor blockers using a novel Two-Shot rat binge drinking model
Update in
-
Greater inhibition of female rat binge alcohol intake by adrenergic receptor blockers using a novel Two-Shot rat binge drinking model.Sci Rep. 2024 Jun 18;14(1):14029. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-64565-9. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38890353 Free PMC article.
Abstract
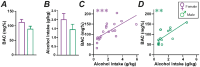
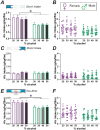
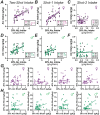
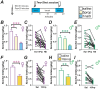
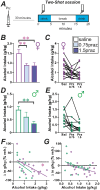
Binge drinking (BD) contributes strongly to the harms of alcohol use disorder. Most rodent models do not result in binge-level blood alcohol concentrations (BACs), and to better understand individual and sex differences in neurobiological mechanisms related to BD, the use of outbred rat strains would be valuable. Here, we developed a novel BD model where after 3+ months of intermittent access to 20% alcohol Wistar rats drank, twice a week, with two 5-minute intake (what we called Two-shot) separated by a 10-minute break. Our findings showed during Two-Shot that most animals reached ≥ 80mg% BAC levels (when briefly food-restricted). However, when increasing alcohol concentrations from 20% to 30%, 40%, or 50%, rats titrated to similar intake levels, suggesting rapid sensing of alcohol effects even when front-loading. Two-Shot drinking was reduced in both sexes by naltrexone (1mg/kg), validating intake suppression by a clinical therapeutic agent. Further, both propranolol (β adrenergic receptor antagonist) and prazosin (α1 adrenergic receptor antagonist) reduced female but not male BD at the lower dose. Thus, our results provide a novel model for BD in outbred rats and suggest that female binging is more sensitive to adrenergic modulation than males, perhaps providing a novel sex-related therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests The authors declare no competing interests. Additional Declarations: No competing interests reported.
Figures

References
-
- CDC, Excessive Drinking Costs U.S. $223.5 Billion. 2014, Center for Disease Control: Atlanta, GA.
-
- Dawson DA, Grant BF, Li TK. Quantifying the risks associated with exceeding recommended drinking limits. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2005; 29:902–8. - PubMed
-
- Jeanblanc J, Sauton P, Jeanblanc V, Legastelois R, Echeverry-Alzate V, Lebourgeois S, Del Carmen Gonzalez-Marin M, Naassila M. Face validity of a pre-clinical model of operant binge drinking: just a question of speed. Addict Biol. 2019; 24:664–675. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

