This is a preprint.
Identification and Characterization of the Lipoprotein N-acyltransferase in Bacteroides
- PMID: 38853980
- PMCID: PMC11160734
- DOI: 10.1101/2024.05.31.596883
Identification and Characterization of the Lipoprotein N-acyltransferase in Bacteroides
Update in
-
Identification and characterization of the lipoprotein N-acyltransferase in Bacteroides.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024 Nov 12;121(46):e2410909121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2410909121. Epub 2024 Nov 4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024. PMID: 39495918 Free PMC article.
Abstract
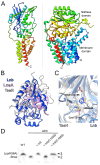
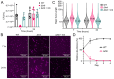
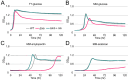
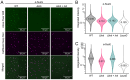
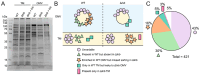
Members of the Bacteroidota compose a large portion of the human gut microbiota, contributing to overall gut health via the degradation of various polysaccharides. This process is facilitated by lipoproteins, globular proteins anchored to the cell surface by a lipidated N-terminal cysteine. Despite their importance, lipoprotein synthesis by these bacteria is understudied. In E. coli, the α-amino linked lipid of lipoproteins is added by the lipoprotein N-acyltransferase Lnt. Herein, we have identified a protein distinct from Lnt responsible for the same process in Bacteroides, named lipoprotein N-acyltransferase in Bacteroides (Lnb). Deletion of Lnb yields cells that synthesize diacylated lipoproteins, with impacts on cell viability and morphology, growth on polysaccharides, and protein composition of membranes and outer membrane vesicles (OMVs). Our results not only challenge the accepted paradigms of lipoprotein biosynthesis in Gram-negative bacteria, but also support the establishment of a new family of lipoprotein N-acyltransferases.
Figures


References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
