This is a preprint.
An Unbiased Proteomic Platform for ATE1-based Arginylation Profiling
- PMID: 38854050
- PMCID: PMC11160793
- DOI: 10.1101/2024.06.01.596974
An Unbiased Proteomic Platform for ATE1-based Arginylation Profiling
Update in
-
An unbiased proteomic platform for ATE1-based arginylation profiling.Nat Chem Biol. 2025 Dec;21(12):1970-1980. doi: 10.1038/s41589-025-01996-z. Epub 2025 Aug 25. Nat Chem Biol. 2025. PMID: 40855110 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Protein arginylation is an essential posttranslational modification (PTM) catalyzed by arginyl-tRNA-protein transferase 1 (ATE1) in mammalian systems. Arginylation features a post-translational conjugation of an arginyl to a protein, making it extremely challenging to differentiate from translational arginine residues with the same mass in a protein sequence. Here we present a general ATE1-based arginylation profiling platform for the unbiased discovery of arginylation substrates and their precise modification sites. This method integrates isotopic arginine labeling into an ATE1 assay utilizing biological lysates (ex vivo) rather than live cells, thus eliminating translational bias derived from the ribosomal activity and enabling bona fide arginylation identification using isotopic features. The method has been successfully applied to an array of peptide, protein, cell, patient, and animal tissue samples using 20 μg sample input, with 235 unique arginylation sites revealed from human proteomes. Representative sites were validated and followed up for their biological functions. The developed platform is globally applicable to the aforementioned sample types and therefore paves the way for functional studies of this difficult-to-characterize protein modification.
Keywords: arginylation; arginyltransferase; posttranslational modification; protein profiling; proteomics.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests Z.L., D.L., and B.A.G. are co-founders of LasNova Therapeutics, LLC.
Figures



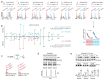

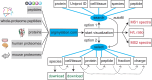
References
-
- Kwon Y. T., Kashina A. S., Davydov I. V., Hu R. G., An J. Y., Seo J. W., Du F. & Varshavsky A. An essential role of N-terminal arginylation in cardiovascular development. Science 297, 96–99, (2002). - PubMed
-
- Kurosaka S., Leu N. A., Pavlov I., Han X., Ribeiro P. A., Xu T., Bunte R., Saha S., Wang J., Cornachione A., Mai W., Yates J. R. 3rd, Rassier D. E. & Kashina A. Arginylation regulates myofibrils to maintain heart function and prevent dilated cardiomyopathy. J Mol Cell Cardiol 53, 333–341, (2012). - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
- R35 GM150678/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD106051/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS102435/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL177113/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R35 HL161185/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG066444/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R21 CA292191/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL141086/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R35 GM122505/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS111997/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK020579/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA054174/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R21 CA286307/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
