This is a preprint.
Active E. coli heteromeric acetyl-CoA carboxylase forms polymorphic helical tubular filaments
- PMID: 38854064
- PMCID: PMC11160672
- DOI: 10.1101/2024.05.28.596234
Active E. coli heteromeric acetyl-CoA carboxylase forms polymorphic helical tubular filaments
Abstract
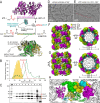
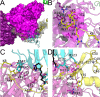
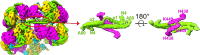
The Escherichia coli heteromeric acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC) has four subunits assumed to form an elusive catalytic complex and are involved in allosteric and transcriptional regulation. The E. coli ACC represents almost all ACCs from pathogenic bacteria making it a key antibiotic development target to fight growing antibiotic resistance. Furthermore, it is a model for cyanobacterial and plant plastid ACCs as biofuel engineering targets. Here we report the catalytic E. coli ACC complex surprisingly forms tubes rather than dispersed particles. The cryo-EM structure reveals key protein-protein interactions underpinning efficient catalysis and how transcriptional regulatory roles are masked during catalysis. Discovering the protein-protein interaction interfaces that facilitate catalysis, allosteric and transcriptional regulation provides new routes to engineering catalytic activity and new targets for drug discovery.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: Authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
