Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension in an Adolescent With Recent Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) Diagnosis: A Challenging Etiological Dilemma
- PMID: 38854218
- PMCID: PMC11162352
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.60001
Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension in an Adolescent With Recent Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) Diagnosis: A Challenging Etiological Dilemma
Abstract
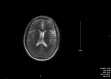
Idiopathic intracranial hypertension (IIH) or benign intracranial hypertension affects the neuro-ophthalmological system and leads to elevated intracranial pressure. Elevated opening pressure during lumbar puncture is diagnostic of IIH. Here in, we present an interesting case of a 15-year-old girl, recently immigrated and with a high BMI, presenting with recurrent fever, abdominal issues, weight loss, and other symptoms, leading to a diagnosis of pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) and HIV infection. After treatment with antibiotics (doxycycline) and antiretroviral therapy, she developed IIH, manifesting as sudden-onset headache and vision problems. MRI and lumbar puncture confirmed the diagnosis. She responded well to acetazolamide and was discharged with continued medication and follow-up appointments. This case underscores the complexity of IIH development, especially in the setting of acute HIV infection and antibiotic treatment, highlighting the need for a comprehensive diagnostic approach and multidisciplinary management.
Keywords: body mass index; doxycycline; hiv; idiopathic intracranial hypertension; lumbar puncture.
Copyright © 2024, Ebong et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Idiopathic intracranial hypertension: consensus guidelines on management. Mollan SP, Davies B, Silver NC, et al. https://scholar.google.com/scholar?q=intitle:Idiopathic%20intracranial%2.... J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2018;89:1088–1100. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Revised diagnostic criteria for the pseudotumor cerebri syndrome in adults and children. Friedman DI, Liu GT, Digre KB. Neurology. 2013;81:1159–1165. - PubMed
-
- Diagnoses of HIV Infection in the United States and Dependent Areas 2019: Special Focus Profiles. 2024. https://www.cdc.gov/hiv/library/reports/hiv-surveillance/vol-32/content/... https://www.cdc.gov/hiv/library/reports/hiv-surveillance/vol-32/content/...
-
- Diagnosis and management of increased intracranial pressure in patients with AIDS and cryptococcal meningitis. Graybill JR, Sobel J, Saag M, et al. https://scholar.google.com/scholar?q=intitle:Diagnosis%20and%20Managemen.... Clin Infect Dis. 2000;30:47–54. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources