Incidence of Unplanned Readmissions After One-Day Surgery Discharge Among Pediatric Patients: A Retrospective Study From a Tertiary Care Hospital in Saudi Arabia
- PMID: 38854243
- PMCID: PMC11160515
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.59896
Incidence of Unplanned Readmissions After One-Day Surgery Discharge Among Pediatric Patients: A Retrospective Study From a Tertiary Care Hospital in Saudi Arabia
Abstract
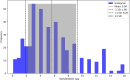
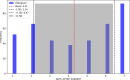
Introduction The prevalence of one-day surgery (also known as same-day surgery or outpatient surgery) has been increasing recently among patients and physicians in many countries due to its benefits. The main benefits of one-day surgery are that the patient is not planned to stay overnight before the surgery and can be discharged on the same day of the surgery. The lower cost to the health system can make these surgeries more favorable for both sides. However, unplanned readmission after such surgeries can happen and this has broad implications for patients, their families, and the healthcare system. Therefore, this study primarily aims to identify the incidence of unexpected hospital readmissions following one-day surgery after discharge among children. The study also aims to identify any significant variables that can be identified with the cases of readmissions to allow for further investigations in future studies Methods This study was done at King Abdullah Specialist Children's Hospital in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia. The target population included all pediatric patients who underwent one-day surgeries and were admitted within one week of their discharge from 2017 to 2023 through outpatient clinics and the emergency department. Results The study sample size was 403 patients, with male patients accounting for 241 surgeries (59.8%), and female patients accounting for 162 surgeries (40.1%). The most common American Society of Anesthesiologists (ASA) classification was II, accounting for 169 cases (41.9%). Toddlers and preschoolers (aged 1-6 years) were the age groups with the highest number of patients (n=252, 62.5% combined). Elective surgeries accounted for 382 cases (94.7%). The specialty with the highest number of surgeries was ear, nose, and throat with 284 cases (70.4%) with tonsillectomy with adenoidectomy being the most common surgery with 234 cases (58%). The most common reasons for unplanned readmission were poor oral intake (n=146, 36.2%) and bleeding (n=131, 32.5%). The most common day of readmission was the seventh day in five surgical specialties (45.4%). Conclusion Over the past seven years, 403 patients were readmitted within one week after their one-day surgery at King Abdullah Specialist Children's Hospital. Such a situation may cause dissatisfaction with the medical care that the patients were given and eventually may build an untrusted relationship between the patient and the physician. Future investigations should be established to lower such a condition and develop prevention methods to lower its prevalence.
Keywords: anesthesia; complication; day surgery; outpatient surgery; same day discharge; unplanned readmission.
Copyright © 2024, Almashari et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Identifying the Prevalence and Causes of 30-Day Hospital Readmission in Children: A Case Study from a Tertiary Pediatric Hospital.Glob J Qual Saf Healthc. 2023 Nov 24;6(4):101-110. doi: 10.36401/JQSH-23-17. eCollection 2023 Nov. Glob J Qual Saf Healthc. 2023. PMID: 38404457 Free PMC article.
-
Rate and Causes of 30-day Unplanned Readmission/Return Following Head and Neck Surgery at a Tertiary Care Center in Saudi Arabia.Saudi J Med Med Sci. 2024 Apr-Jun;12(2):162-168. doi: 10.4103/sjmms.sjmms_138_23. Epub 2024 Apr 5. Saudi J Med Med Sci. 2024. PMID: 38764562 Free PMC article.
-
Unplanned readmission within 90 days after pediatric neurosurgery.J Neurosurg Pediatr. 2017 Dec;20(6):542-548. doi: 10.3171/2017.6.PEDS17117. Epub 2017 Oct 13. J Neurosurg Pediatr. 2017. PMID: 29027867
-
Unplanned Readmissions in Children with Medical Complexity in Saudi Arabia: A Large Multicenter Study.Saudi J Med Med Sci. 2024 Apr-Jun;12(2):134-144. doi: 10.4103/sjmms.sjmms_352_23. Epub 2024 Apr 5. Saudi J Med Med Sci. 2024. PMID: 38764560 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive review of a large cohort of outpatient versus inpatient open renal and bladder surgery in children.J Pediatr Urol. 2023 Aug;19(4):432.e1-432.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.jpurol.2023.04.033. Epub 2023 May 4. J Pediatr Urol. 2023. PMID: 37210299 Review.
Cited by
-
The Impact of Preoperative Risk Factors on Unplanned Readmission After Day Surgery: A Meta-Analysis.J Pers Med. 2025 Jul 1;15(7):281. doi: 10.3390/jpm15070281. J Pers Med. 2025. PMID: 40710398 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Pediatric tonsillectomy is a resource-intensive procedure: a study of Canadian health administrative data. Murto KT, Katz SL, McIsaac DI, Bromwich MA, Vaillancourt R, van Walraven C. Can J Anaesth. 2017;64:724–735. - PubMed
-
- Unanticipated admission after ambulatory surgery in the pediatric population: a single-center retrospective analysis. Van Caelenberg E, Benoit D, Verhaeghe R, Coppens M. Acta Chir Belg. 2022;122:178–184. - PubMed
-
- Unplanned hospital admission in children undergoing day-case surgery. Awad IT, Moore M, Rushe C, Elburki A, O'Brien K, Warde D. Eur J Anaesthesiol. 2004;21:379–383. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
