Ozone Disc Nucleolysis for Cervical Intervertebral Disc Herniation: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 38854278
- PMCID: PMC11162285
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.59855
Ozone Disc Nucleolysis for Cervical Intervertebral Disc Herniation: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
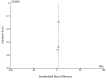
Cervical intervertebral disc herniation is a common condition and most often presents as neck or upper limb pain causing varying levels of disability and dysfunction. Percutaneous injection of ozone into the intradiscal space is a novel and minimally invasive technique for managing this condition and can be an effective alternative to surgical management. A literature search was done using the keywords ozone disc nucleolysis of cervical intervertebral lesions, and five studies were selected based on the inclusion and exclusion criteria. Meta-analysis was performed to determine safety, effectiveness, and symptomatic relief (determined based on the visual analog scale (VAS)) with the publication bias being removed. Subjects treated with ozone therapy showed significant reduction (p < 0.0001) in VAS score as compared to baseline VAS score with a standardized mean difference of 2.78 (95% CI = 1.48 to 4.07; Z value = 4.20). Ozone nucleolysis is a minimally invasive, relatively safe, and optimally effective treatment option for reducing the pain related to cervical disc. Intradiscal ozone therapy can be considered an alternative treatment modality, and well-designed, randomized clinical trials are required to confirm the long-term superiority of ozone therapy against other treatment modalities available for cervical disc herniation.
Keywords: cervical disc herniation; cervical radiculopathy; chemonucleolysis; intradiscal injection; oxygen-ozone mixture.
Copyright © 2024, Ghatge et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
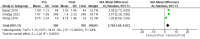
Similar articles
-
Ozone disc nucleolysis in cervical intervertebral disc herniation: A nonrandomized prospective analysis in 246 patients.J Craniovertebr Junction Spine. 2022 Apr-Jun;13(2):114-120. doi: 10.4103/jcvjs.jcvjs_46_22. Epub 2022 Jun 13. J Craniovertebr Junction Spine. 2022. PMID: 35837424 Free PMC article.
-
Intradiscal oxygen-ozone chemonucleolysis versus microdiscectomy for lumbar disc herniation radiculopathy: a non-inferiority randomized control trial.Spine J. 2022 Jun;22(6):895-909. doi: 10.1016/j.spinee.2021.11.017. Epub 2021 Dec 9. Spine J. 2022. PMID: 34896609 Clinical Trial.
-
Ozone disc nucleolysis in the management of herniated lumbar intervertebral disc: A retrospective analysis.J Craniovertebr Junction Spine. 2023 Jan-Mar;14(1):16-23. doi: 10.4103/jcvjs.jcvjs_141_22. Epub 2023 Mar 13. J Craniovertebr Junction Spine. 2023. PMID: 37213581 Free PMC article.
-
Intradiscal O2O3: Rationale, Injection Technique, Short- and Long-term Outcomes for the Treatment of Low Back Pain Due to Disc Herniation.Can Assoc Radiol J. 2017 May;68(2):171-177. doi: 10.1016/j.carj.2016.12.007. Can Assoc Radiol J. 2017. PMID: 28438284 Review.
-
Minimally Invasive Percutaneous Techniques for the Treatment of Cervical Disc Herniation: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.J Clin Med. 2025 May 8;14(10):3280. doi: 10.3390/jcm14103280. J Clin Med. 2025. PMID: 40429275 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Comparison of chemonucleolysis and discectomy in the management of lumbar disc herniation: a comprehensive systematic review and meta-analysis.Neurosurg Rev. 2025 Apr 3;48(1):347. doi: 10.1007/s10143-025-03501-5. Neurosurg Rev. 2025. PMID: 40175852
-
Collagenase Chemonucleolysis for Treating Cervical Disc Herniation: An Exploratory, Single-Arm, Open-Label, Multicenter Clinical Trial.Pain Ther. 2025 Feb;14(1):217-235. doi: 10.1007/s40122-024-00678-3. Epub 2024 Nov 8. Pain Ther. 2025. PMID: 39514049 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sharrak S, Al Khalili Y. Cervical disc herniation. 2023. In: StatPearls [Internet] Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023. Cervical Disc Herniation. - PubMed
-
- Interventional spinal procedures. Andreula C, Muto M, Leonardi M. Eur J Radiol. 2004;50:112–119. - PubMed
-
- Percutaneous treatment of herniated lumbar discs with ozone: Investigation of the mechanisms of action. Murphy K, Elias G, Steppan J, et al. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2016;27:1242–1250. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
