Wilson Disease in Children in the Eastern Region of Morocco: Analysis of 24 Cases
- PMID: 38854322
- PMCID: PMC11162554
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.60023
Wilson Disease in Children in the Eastern Region of Morocco: Analysis of 24 Cases
Abstract
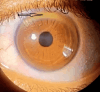
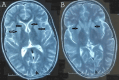
Wilson's disease (WD), or "hepato-lenticular degeneration," is a rare genetic disorder of autosomal recessive inheritance causing toxic tissue accumulation of copper, mainly in the liver, brain, and cornea. Its phenotypic and genotypic heterogeneity characterizes it. This study aimed to clarify the clinical features and spectrum of Wilson's disease in children from the eastern region of Morocco and to study the evolutionary profile and survival in this population while discussing and highlighting the various diagnostic and therapeutic difficulties encountered in the management of WD in our context. This retrospective study encompassed 24 children diagnosed with Wilson's disease, selected from the gastroenterology-hepatology and pediatric nutrition units at Mohamed VI University Hospital in Oujda, Morocco, over a span of nine years, from January 2015 to November 2023. Our series results show 14 boys and 10 girls; the median age of discovery was 11 years, with extremes ranging from 18 months to 15 years. The consanguinity was found in 13 patients. Clinically, the edemato-ascitic syndrome was noted in 14 patients with an alteration of the general state; icterus was found in 13 patients; signs of portal hypertension were present in six patients; and neurological signs in seven cases. Skin manifestations occurred in three cases, and arthralgia in three cases. Six children were diagnosed on the occasion of a family screening. Biologically, hepatic cytolysis was found in 20 patients, with signs of hepatocellular failure in 15 cases. Hemolytic anemia was present in nine patients. Ceruloplasminemia was decreased in 21 patients and cupremia in 19 patients. Cupruria was increased in 22 cases. The Kayser-Fleicher ring was found in 10 cases. Abdominal ultrasound showed ascites in 16 patients, hepatomegaly in 1, splenomegaly in two cases, hepatosplenomegaly in five cases, and cirrhosis in two. MRI showed signal abnormalities in 11 patients. Therapeutically, D-penicillamine was initially introduced in 18 patients and zinc acetate in 6 patients. The evolution was favorable for 15 patients still followed up in the department. Three patients died of hepatocellular failure, and two died of hepatic encephalopathy. Four patients were lost to follow-up.
Keywords: atp7b mutations; central nervous system; child; copper; d-penicillamine; hepatopathy; kayser-fleischer ring; screening.; wilson.
Copyright © 2024, Rkain et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Epidemiology, clinical features, and mortality rate of Wilson disease in Moroccan children: A pediatric case series.Arch Pediatr. 2022 Aug;29(6):453-458. doi: 10.1016/j.arcped.2022.03.010. Epub 2022 Jun 12. Arch Pediatr. 2022. PMID: 35705388
-
[The onset of psychiatric disorders and Wilson's disease].Encephale. 2007 Dec;33(6):924-32. doi: 10.1016/j.encep.2006.08.009. Epub 2007 Sep 5. Encephale. 2007. PMID: 18789784 French.
-
Childhood Wilson Disease: Bangladesh Perspective.Mymensingh Med J. 2017 Apr;26(2):406-413. Mymensingh Med J. 2017. PMID: 28588179
-
Wilson's Disease: Clinical Practice Guidelines of the Indian National Association for Study of the Liver, the Indian Society of Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition, and the Movement Disorders Society of India.J Clin Exp Hepatol. 2019 Jan-Feb;9(1):74-98. doi: 10.1016/j.jceh.2018.08.009. Epub 2018 Sep 3. J Clin Exp Hepatol. 2019. PMID: 30765941 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Wilson's disease.Clin Liver Dis. 1998 Feb;2(1):31-49, v-vi. doi: 10.1016/s1089-3261(05)70362-7. Clin Liver Dis. 1998. PMID: 15560044 Review.
Cited by
-
The Importance of Genetic Testing: A Case Report of Wilson's Disease in Two Siblings of a Three-Sibling Family.Cureus. 2025 Jan 23;17(1):e77891. doi: 10.7759/cureus.77891. eCollection 2025 Jan. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 39996228 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wilson disease in children and adolescents. Fernando M, van Mourik I, Wassmer E, Kelly D. Arch Dis Child. 2020;105:499–505. - PubMed
-
- Maladie de Wilson. Poujois A, Djebrani-Oussedik N, Poupon J. Revue Francophone des Laboratoires. 2021;533:44.
-
- Wilson disease: an overview and approach to management. Mulligan C, Bronstein JM. Neurol Clin. 2020;38:417–432. - PubMed
-
- Maladie de Wilson. Woimant F, Trocello JM, Girardot-Tinant N, et al. EMC - Neurologie. 2013;10:1–14.
-
- Maladie de Wilson. Lacaille F. EMC - Hépatologie. 2009;7:210.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources