Optimizing Diagnostic Performance of ChatGPT: The Impact of Prompt Engineering on Thoracic Radiology Cases
- PMID: 38854352
- PMCID: PMC11162509
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.60009
Optimizing Diagnostic Performance of ChatGPT: The Impact of Prompt Engineering on Thoracic Radiology Cases
Abstract
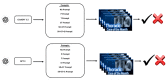
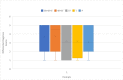
Background Recent studies have highlighted the diagnostic performance of ChatGPT 3.5 and GPT-4 in a text-based format, demonstrating their radiological knowledge across different areas. Our objective is to investigate the impact of prompt engineering on the diagnostic performance of ChatGPT 3.5 and GPT-4 in diagnosing thoracic radiology cases, highlighting how the complexity of prompts influences model performance. Methodology We conducted a retrospective cross-sectional study using 124 publicly available Case of the Month examples from the Thoracic Society of Radiology website. We initially input the cases into the ChatGPT versions without prompting. Then, we employed five different prompts, ranging from basic task-oriented to complex role-specific formulations to measure the diagnostic accuracy of ChatGPT versions. The differential diagnosis lists generated by the models were compared against the radiological diagnoses listed on the Thoracic Society of Radiology website, with a scoring system in place to comprehensively assess the accuracy. Diagnostic accuracy and differential diagnosis scores were analyzed using the McNemar, Chi-square, Kruskal-Wallis, and Mann-Whitney U tests. Results Without any prompts, ChatGPT 3.5's accuracy was 25% (31/124), which increased to 56.5% (70/124) with the most complex prompt (P < 0.001). GPT-4 showed a high baseline accuracy at 53.2% (66/124) without prompting. This accuracy increased to 59.7% (74/124) with complex prompts (P = 0.09). Notably, there was no statistical difference in peak performance between ChatGPT 3.5 (70/124) and GPT-4 (74/124) (P = 0.55). Conclusions This study emphasizes the critical influence of prompt engineering on enhancing the diagnostic performance of ChatGPT versions, especially ChatGPT 3.5.
Keywords: chat generative pre-trained transformer (chatgpt); gpt-4; large language models; prompt engineering; radiology.
Copyright © 2024, Cesur et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures



References
-
- Large language models in medicine. Thirunavukarasu AJ, Ting DS, Elangovan K, Gutierrez L, Tan TF, Ting DS. Nat Med. 2023;29:1930–1940. - PubMed
-
- Gunes YC, Cesur T. A Comparative Study: Diagnostic Performance of ChatGPT 3.5, Google Bard, Microsoft Bing, and Radiologists in Thoracic Radiology Cases. A Comparative Study: Diagnostic Performance of ChatGPT 3.5, Google Bard, Microsoft Bing, and Radiologists in Thoracic Radiology Cases. medRxiv [preprint. [ Feb; 2024 ]. 2024. https://doi.org/10.1101/2024.01.18.24301495 https://doi.org/10.1101/2024.01.18.24301495
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
