Combined evaluation of glomerular phospholipase A2 receptor and immunoglobulin G subclass in membranous nephropathy
- PMID: 38854426
- PMCID: PMC11161704
- DOI: 10.1093/ckj/sfae104
Combined evaluation of glomerular phospholipase A2 receptor and immunoglobulin G subclass in membranous nephropathy
Abstract
Background: Phospholipase A2 receptor (PLA2R) is a major target antigen in idiopathic membranous nephropathy (MN). Anti-PLA2R antibodies are mainly of the immunoglobulin G (IgG) subclass IgG4, although other IgG subclass depositions in glomeruli may also be detected. However, the importance of the subclass of the IgG deposit has not been proven. Thus we investigated clinical findings from patients with idiopathic MN in relation to glomerular PLA2R deposition and IgG subclass.
Methods: We enrolled 132 Japanese patients with biopsy-proven idiopathic MN in a multicentre retrospective observational study. We investigated the complete remission rate as the primary outcome and the development of end-stage kidney disease (ESKD) as the secondary outcome in relation to glomerular PLA2R deposition. Moreover, we evaluated prognostic factors, including glomerular IgG subclass, in the PLA2R-positive group.
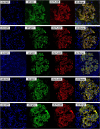
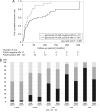
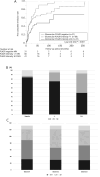
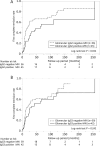
Results: The percentage of cases with glomerular PLA2R deposition was 76.5% (n = 101). The first complete remission rate of the PLA2R-positive group was worse than that of the PLA2R-negative group (logrank test P < .001). ESKD incidence did not significantly differ between the glomerular PLA2R-negative and PLA2R-positive MN groups (logrank test P = .608). In the PLA2R-positive group, higher PLA2R intensities and IgG2 staining were associated with a poorer first complete remission rate (logrank test P < .001 and P = .032, respectively). Cox proportional hazards analysis also showed that strong PLA2R deposition and positive IgG2 staining were significantly associated with a failure to reach complete remission [hazard ratio 2.09 (P = .004) and 1.78 (P = .030), respectively].
Conclusions: Our results suggest that intense glomerular PLA2R and IgG2 positivity predict a poor proteinuria remission rate in idiopathic MN.
Keywords: complement; immunoglobulin G subclass; membranous nephropathy; oligosaccharide; phospholipase A2 receptor.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the ERA.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Clinicopathological characteristics of M-type phospholipase A2 receptor (PLA2R)-related membranous nephropathy in Japanese.Clin Exp Nephrol. 2015 Oct;19(5):797-803. doi: 10.1007/s10157-014-1064-0. Epub 2014 Dec 10. Clin Exp Nephrol. 2015. PMID: 25492250
-
Analysis of Glomerular IgG Subclasses Switch in Idiopathic Membranous Nephropathy Classified by Glomerular Phospholipase A2 Receptor Antigen and Serum Antibody.Dis Markers. 2021 Aug 30;2021:9965343. doi: 10.1155/2021/9965343. eCollection 2021. Dis Markers. 2021. PMID: 34497677 Free PMC article.
-
Glomerular IgG subclasses in idiopathic and malignancy-associated membranous nephropathy.Clin Kidney J. 2015 Aug;8(4):433-9. doi: 10.1093/ckj/sfv049. Epub 2015 Jul 9. Clin Kidney J. 2015. PMID: 26251712 Free PMC article.
-
Clinicopathological features in membranous nephropathy with cancer: A retrospective single-center study and literature review.Int J Biol Markers. 2019 Dec;34(4):406-413. doi: 10.1177/1724600819882698. Epub 2019 Oct 16. Int J Biol Markers. 2019. PMID: 31617780 Review.
-
Clinical usefulness of autoantibodies to M-type phospholipase A2 receptor (PLA2R) for monitoring disease activity in idiopathic membranous nephropathy (IMN).Autoimmun Rev. 2016 Feb;15(2):146-54. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2015.10.004. Epub 2015 Oct 23. Autoimmun Rev. 2016. PMID: 26527329 Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

