Morphology and Thermodynamic Study of a Novel Composite Membrane from Waste Polystyrene/Slag: Experimental Investigation
- PMID: 38854541
- PMCID: PMC11154918
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.4c00671
Morphology and Thermodynamic Study of a Novel Composite Membrane from Waste Polystyrene/Slag: Experimental Investigation
Abstract
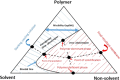
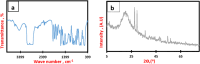
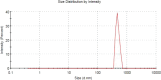
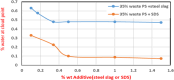
The development of the membrane surface and cross-sectional morphology is pivotal in influencing the effectiveness of membrane separation. In this study, evaluating the separation rates between the solvent and nonsolvent in the casting solution and the related thermodynamic alteration analysis were illustrated. Additionally, the rheological variations were determined by measuring the viscosity of the resulting dope solutions, providing an initial estimation of the phase separation kinetics. Asymmetric polystyrene (PS)/slag composite membrane, incorporating slag waste as an inorganic additive, was developed. Dimethylformamide (DMF) was utilized as the solvent, and sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) was employed as an anionic surfactant to facilitate the casting process. A tertiary system diagram approach involving waste PS, DMF, and water introducing slag as an inorganic additive and SDS as a surfactant was attained to promote the separation of the solvent and nonsolvent in the casting solution. These novel composite mixtures exhibited increased thermodynamic instability within the coagulation bath, facilitating the rapid separation of solid membranes from the dope solutions and forming composite membranes with significantly increased porosity (exceeding a 20% increase) compared to that of plain waste materials. The composite membrane characteristics were assessed with the widely used poly(vinylidene difluoride) (PVDF) membrane, showing comparative features and performance when tested on a membrane distillation (MD) cell; it gave a flux of 1 kg/m2·h. These promising characteristics positioned this novel PS/slag composite membrane as a candidate for various water-related applications.
© 2024 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures



References
-
- Achilias D. S.; Andriotis L.; Koutsidis I. A.; Louka D. A.; Nianias N. P.; Siafaka P.; Tsagkalias I.; Tsintzou G.. Recent Advances in the Chemical Recycling of Polymers (PP, PS, LDPE, HDPE, PVC, PC, Nylon, PMMA). In Material Recycling; Achilias D. S., Ed.; IntechOpen: Rijeka, 2012.
-
- Zhuang G. L.; Tseng H.-H.; Wey M. Y. Feasibility of using waste polystyrene as a membrane material for gas separation. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2016, 111, 204–217. 10.1016/j.cherd.2016.03.033. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
