Predictive Value of Smoking Index Combined with NT-proBNP for Patients with Pulmonary Hypertension Due to Chronic Lung Disease: A Retrospective Study
- PMID: 38854590
- PMCID: PMC11162191
- DOI: 10.2147/COPD.S448496
Predictive Value of Smoking Index Combined with NT-proBNP for Patients with Pulmonary Hypertension Due to Chronic Lung Disease: A Retrospective Study
Abstract
Purpose: Smoking is a major risk factor for the group 3 PH. NT-proBNP is a biomarker for risk stratification in PH. This study aims to investigate the effects of smoking status and smoking index (SI) on group 3 PH and to evaluate the value of SI and SI combined with NT-proBNP in early diagnosis and prediction of disease severity.
Patients and methods: Four hundred patients with group 3 PH at the First Hospital of Shanxi Medical University between January 2020 and December 2021 were enrolled and divided into two groups: mild (30 mmHg ≤ pulmonary artery systolic pressure (PASP)≤50 mmHg) and non-mild (PASP >50 mmHg). The effect of smoking on group 3 PH was analyzed using univariate analysis, and logistic analysis was conducted to evaluate the risk of group 3 PH according to smoking status and SI. Spearman correlation coefficient was used to test the correlation between SI and the index of group 3 PH severity. The predictive value of SI was evaluated using a receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve.
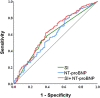
Results: Correlation and logistic analyses showed that SI was associated with PH severity. Smoking status (P=0.009) and SI (P=0.039) were independent risk factors for non-mild group 3 PH, and ROC showed that the predictive value of SI (AUC:0.596) for non-mild PH was better than that of the recognized pro-brain natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) (AUC:0.586). SI can be used as a single predictive marker. SI and NT-proBNP can be formulated as prediction models for screening non-mild clinical cases (AUC:0.628).
Conclusion: SI is a potentially ideal non-invasive predictive marker for group 3 PH. SI and NT-proBNP could be used to develop a prediction model for screening non-mild PH cases. This can greatly improve the predictive specificity of the established PH marker, NT-proBNP.
Keywords: NT-proBNP; chronic lung disease; predictive value; pulmonary hypertension; smoking index.
© 2024 Sun et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures

Similar articles
-
B-type natriuretic peptide as a parameter for pulmonary hypertension in children. A systematic review.Eur J Pediatr. 2015 Oct;174(10):1267-75. doi: 10.1007/s00431-015-2619-0. Epub 2015 Aug 23. Eur J Pediatr. 2015. PMID: 26298682
-
The comparative and added prognostic value of biomarkers to the Revised Cardiac Risk Index for preoperative prediction of major adverse cardiac events and all-cause mortality in patients who undergo noncardiac surgery.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Dec 21;12(12):CD013139. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013139.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 34931303 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical value of combined detection of serum ferritin and N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide in the assessment of Kawasaki disease in children over 1 year of age.Ital J Pediatr. 2025 Jul 15;51(1):229. doi: 10.1186/s13052-025-02076-7. Ital J Pediatr. 2025. PMID: 40660372 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic MicroRNA Signatures to Support Classification of Pulmonary Hypertension.Circ Genom Precis Med. 2025 Jun;18(3):e004862. doi: 10.1161/CIRCGEN.124.004862. Epub 2025 Apr 18. Circ Genom Precis Med. 2025. PMID: 40248872 Free PMC article.
-
Brain natriuretic peptide and N-terminal brain natriuretic peptide for the diagnosis of haemodynamically significant patent ductus arteriosus in preterm neonates.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Dec 8;12(12):CD013129. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013129.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36478359 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

