Challenging of ECMO application in pediatric restrictive cardiomyopathy: case report of a novel TNNI3 variant
- PMID: 38854656
- PMCID: PMC11157066
- DOI: 10.3389/fcvm.2024.1365209
Challenging of ECMO application in pediatric restrictive cardiomyopathy: case report of a novel TNNI3 variant
Abstract
Background: Restrictive cardiomyopathy (RCM) represents a rare cardiovascular disorder stemming from filament-associated genes. Nonetheless, treating RCM presents considerable challenges, particularly concerning device implantation and mechanical support. Furthermore, elucidating the molecular function of specific variants holds promise in benefiting patients and enhancing prognosis, given the significant heterogeneity among RCM variants.
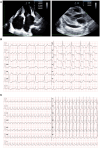
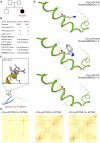
Case presentation: The proband, an eight-year-old female, was admitted to our hospital post cardiopulmonary resuscitation due to sudden cardiac arrest. Echocardiography revealed bilateral atrial enlargement. Whole-exome sequencing uncovered a novel heterozygous mutation (c.509G>A, p.R170Q) in TNNI3. Evaluation using the MutationTaster application deemed c.509G>A pathogenic (probability = 0.99). Following clinical manifestations, imaging assessments, and genetic screening, the proband received an RCM diagnosis. ECMO was recommended along with continuous renal replacement therapy. However, persistent atrial flutter ensued post-ECMO withdrawal. Attempts to restore cardiac rhythm with cardioversion, metoprolol, and amiodarone proved futile. Subsequent heart failure led to the patient's demise due to cardiac shock. Based on crystal protein structural analysis, we observed that cTnI-R170Q and R170W exerted similar impacts on protein structural stability and formation. However, both differed significantly from cTnI-R170G, primarily influencing amino acid regions 32-79 and 129-149, involved in TnC and actin binding. Therefore, cTnI-R170Q was revealed to induce RCM via the same molecular mechanism as cTnI-R170W.
Conclusion: Managing RCM remains a critical challenge. This study underscores the discouragement of device implantations for cardiac pump functional support in RCM, particularly for non-short-term scheduled HTx. Additionally, considering catheter ablation for atrial fibrosis-induced AFs is recommended. Mechanistically, cTnI-R170Q primarily diminishes troponin-actin interactions and destabilizes thin filaments.
Keywords: ECMO; TNNI3; heart failure; heart transplantation; restrictive cardiomyopathy.
© 2024 Jin, Xu, Hua, Zhang and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

