Comprehensive machine learning models for predicting therapeutic targets in type 2 diabetes utilizing molecular and biochemical features in rats
- PMID: 38854687
- PMCID: PMC11157016
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1384984
Comprehensive machine learning models for predicting therapeutic targets in type 2 diabetes utilizing molecular and biochemical features in rats
Abstract
Introduction: With the increasing prevalence of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), there is an urgent need to discover effective therapeutic targets for this complex condition. Coding and non-coding RNAs, with traditional biochemical parameters, have shown promise as viable targets for therapy. Machine learning (ML) techniques have emerged as powerful tools for predicting drug responses.
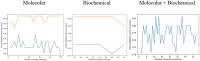
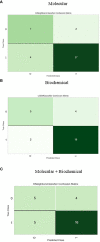
Method: In this study, we developed an ML-based model to identify the most influential features for drug response in the treatment of type 2 diabetes using three medicinal plant-based drugs (Rosavin, Caffeic acid, and Isorhamnetin), and a probiotics drug (Z-biotic), at different doses. A hundred rats were randomly assigned to ten groups, including a normal group, a streptozotocin-induced diabetic group, and eight treated groups. Serum samples were collected for biochemical analysis, while liver tissues (L) and adipose tissues (A) underwent histopathological examination and molecular biomarker extraction using quantitative PCR. Utilizing five machine learning algorithms, we integrated 32 molecular features and 12 biochemical features to select the most predictive targets for each model and the combined model.
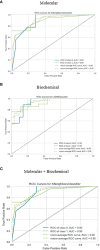
Results and discussion: Our results indicated that high doses of the selected drugs effectively mitigated liver inflammation, reduced insulin resistance, and improved lipid profiles and renal function biomarkers. The machine learning model identified 13 molecular features, 10 biochemical features, and 20 combined features with an accuracy of 80% and AUC (0.894, 0.93, and 0.896), respectively. This study presents an ML model that accurately identifies effective therapeutic targets implicated in the molecular pathways associated with T2DM pathogenesis.
Keywords: drug response; machine learning; rats; therapeutic targets; type 2 diabetes.
Copyright © 2024 Matboli, Al-Amodi, Khaled, Khaled, Roushdy, Ali, Diab, Elnagar, Elmansy, TAhmed, Ahmed, Elzoghby, M.Kamel, Farag, ELsawi, Farid, Abouelkhair, Habib, Fikry, Saleh and Aboughaleb.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Ray KK, Nicholls SJ, Li N, Louie MJ, Brennan D, Lincoff AM, et al. . Efficacy and safety of bempedoic acid among patients with and without diabetes: prespecified analysis of the CLEAR Outcomes randomised trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinology. (2024) 12:19–28. doi: 10.1016/S2213-8587(23)00316-9 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Antonio-Villa NE, Fernández-Chirino L, Vargas-Vazquez A, Bahena-López JP, Bello-Chavolla OY. Trends in diabetes subgroups and their risk for all-cause, cardiovascular disease and diabetes-specific mortality in the US: A data-driven reproducible machine learning approach. J Endocrine Soc. (2021) 5:A423. doi: 10.1210/jendso/bvab048.863 - DOI
-
- Buse JB, Wexler DJ, Tsapas A, Rossing P, Mingrone G, Mathieu C, et al. . 2019 update to: management of hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetes, 2018. A consensus report by the American Diabetes Association (ADA) and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD). Diabetes Care. (2020) 43:487–93. doi: 10.2337/dci19-0066 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

