Development and validation of nomogram to predict overall survival and disease-free survival after surgical resection in elderly patients with hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 38854717
- PMCID: PMC11157056
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1395740
Development and validation of nomogram to predict overall survival and disease-free survival after surgical resection in elderly patients with hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
Background: Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is one of the common causes of tumor death in elderly patients. However, there is a lack of individualized prognostic predictors for elderly patients with HCC after surgery.
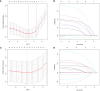
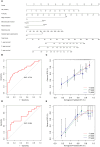
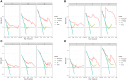
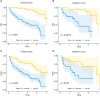
Method: We retrospectively analyzed HCC patients over 65 years old who underwent hepatectomy from 2015 to 2018, and randomly divided them into training cohort and validation cohort in a ratio of 3:1. Univariate Cox regression was used to screen the risk factors related to prognosis. Prognostic variables were further selected by least absolute shrinkage and selection operator regression model (LASSO) and multivariate Cox regression to identify the predictors of overall survival (OS) and disease-free survival (DFS). These indicators were then used to construct a predictive nomogram. The receiver operating characteristic curve (ROC curve), calibration curve, consistency index (C-index) and decision analysis curve (DCA) were used to test the predictive value of these independent prognostic indicators.
Result: A total of 188 elderly HCC patients who underwent hepatectomy were enrolled in this study. The independent prognostic indicators of OS included albumin (ALB), cancer embolus, blood loss, viral hepatitis B, total bilirubin (TB), microvascular invasion, overweight, and major resection. The independent prognostic indicators of DFS included major resection, ALB, microvascular invasion, laparoscopic surgery, blood loss, TB, and pleural effusion. In the training cohort, the ROC curve showed that the predictive values of these indicators for OS and DFS were 0.827 and 0.739, respectively, while in the validation cohort, they were 0.798 and 0.694. The calibration curve nomogram exhibited good prediction for 1-year, 2-year, and 3-year OS and DFS. Moreover, the nomogram models exhibited superior performance compared to the T-staging suggested by C-index and DCA.
Conclusion: The nomogram established in this study demonstrate commendable predictive efficacy for OS and DFS in elderly patients with HCC after hepatectomy.Core Tip: The purpose of this retrospective study is to screen the risk factors of survival and recurrence in elderly patients with HCC after hepatectomy. The nomogram included cancer embolus, viral hepatitis B, overweight, major resection, ALB, microvascular invasion, laparoscopic surgery, blood loss, TB, and pleural effusion as predictors. The calibration curve of this nomogram was good, indicating credible predictive value and clinical feasibility.
Keywords: elderly; hepatocellular carcinoma; nomogram; prognosis; recurrence.
Copyright © 2024 Tian, Wang, Wen, Lin, Liu and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Prognostic value of preoperative systemic immune-inflammation index/albumin for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma undergoing curative resection.World J Gastroenterol. 2024 Dec 28;30(48):5130-5151. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i48.5130. World J Gastroenterol. 2024. PMID: 39735268 Free PMC article.
-
A radiomics nomogram for the prediction of overall survival in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma after hepatectomy.Cancer Imaging. 2020 Nov 16;20(1):82. doi: 10.1186/s40644-020-00360-9. Cancer Imaging. 2020. PMID: 33198809 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Preoperative contrast-enhanced computed tomography-based radiomics model for overall survival prediction in hepatocellular carcinoma.World J Gastroenterol. 2022 Aug 21;28(31):4376-4389. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i31.4376. World J Gastroenterol. 2022. PMID: 36159012 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
A CECT-Based Radiomics Nomogram Predicts the Overall Survival of Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma After Surgical Resection.Biomedicines. 2025 May 19;13(5):1237. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines13051237. Biomedicines. 2025. PMID: 40427064 Free PMC article.
-
Development and Validation of a Risk Prediction Model Based on Inflammatory and Nutritional Composite Indicators for Posthepatectomy Liver Failure Following Radical Resection of Hepatocellular Carcinoma.J Inflamm Res. 2025 Apr 18;18:5261-5279. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S515918. eCollection 2025. J Inflamm Res. 2025. PMID: 40270559 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Refining MR-guided thermal ablation for HCC within the Milan criteria: a decade of clinical outcomes and predictive modeling at a single institution.BMC Cancer. 2025 Jan 28;25(1):159. doi: 10.1186/s12885-025-13510-8. BMC Cancer. 2025. PMID: 39875824 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

