The safety and feasibility of laparoscopic anatomical left hemihepatectomy along the middle hepatic vein from the head side approach
- PMID: 38854724
- PMCID: PMC11157031
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1368678
The safety and feasibility of laparoscopic anatomical left hemihepatectomy along the middle hepatic vein from the head side approach
Abstract
Background: Laparoscopic left hemihepatectomy (LLH) is commonly used for benign and malignant left liver lesions. We compared the benefits and drawbacks of LLH from the head side approach (LLHH) with those of conventional laparoscopic left hemihepatectomy (CLLH). This study was conducted to investigate the safety and feasibility of LLHH by comparing it with CLLH.
Methods: In this study, 94 patients with tumor or hepatolithiasis who underwent LLHH (n = 39) and CLLH (n = 55) between January 2016 and January 2023 were included. The preoperative features, intraoperative details, and postoperative outcomes were compared between the two groups.
Results: For hepatolithiasis, patients who underwent LLHH exhibited shorter operative time (p = 0.035) and less blood loss (p = 0.023) than those who underwent CLLH. However, for tumors, patients undergoing LLHH only showed shorter operative time (p = 0.046) than those undergoing CLLH. Moreover, no statistically significant differences in hospital stay, transfusion, hospital expenses, postoperative white blood cell (WBC) count, alanine aminotransferase (ALT), and aspartate aminotransferase (AST) were observed between the two groups (p > 0.05) for tumor or hepatolithiasis. For hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), no differences in both overall survival (p = 0.532) and disease-free survival (p = 0.274) were observed between the two groups.
Conclusion: LLHH is a safe and feasible surgical procedure for tumors or hepatolithiasis of the left liver.
Keywords: hepatectomy; hepatolithiasis; laparoscopic; left hemihepatectomy; survival.
Copyright © 2024 Li, Fang and Huang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

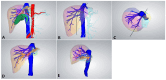
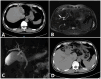
Similar articles
-
Comparison of laparoscopic versus open left hemihepatectomy for left-sided hepatolithiasis.Int J Med Sci. 2014 Jan 2;11(2):127-33. doi: 10.7150/ijms.7516. eCollection 2014. Int J Med Sci. 2014. PMID: 24465157 Free PMC article.
-
Laparoscopic versus open left hemihepatectomy for hepatolithiasis.J Surg Res. 2015 Dec;199(2):402-6. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2015.06.021. Epub 2015 Jun 16. J Surg Res. 2015. PMID: 26169034
-
Laparoscopic left-sided hepatectomy for the treatment of hepatolithiasis: A comparative study with open approach.Int J Surg. 2017 Apr;40:117-123. doi: 10.1016/j.ijsu.2017.02.068. Epub 2017 Feb 28. Int J Surg. 2017. PMID: 28254607
-
Fully laparoscopic left hepatectomy - a technical reference proposed for standard practice compared to the open approach: a retrospective propensity score model.HPB (Oxford). 2018 Apr;20(4):347-355. doi: 10.1016/j.hpb.2017.10.006. Epub 2017 Nov 21. HPB (Oxford). 2018. PMID: 29169905 Review.
-
Comparison of the Safety and Efficacy of Laparoscopic Left Lateral Hepatectomy and Open Left Lateral Hepatectomy for Hepatolithiasis: A Meta-Analysis.Front Surg. 2021 Nov 16;8:749285. doi: 10.3389/fsurg.2021.749285. eCollection 2021. Front Surg. 2021. PMID: 34869557 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

