Dupilumab improves outcomes in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps irrespective of gender: results from the SINUS-52 trial
- PMID: 38854740
- PMCID: PMC11161870
- DOI: 10.1002/cti2.1511
Dupilumab improves outcomes in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps irrespective of gender: results from the SINUS-52 trial
Abstract
Objectives: This post hoc analysis assessed disease characteristics and response to dupilumab treatment in male and female patients with severe chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps (CRSwNP) (SINUS-52 study; NCT02898454).
Methods: Patients received dupilumab 300 mg or placebo every 2 weeks for 52 weeks on background intranasal corticosteroids. Efficacy was assessed through Week 52 using nasal polyp score (NPS), nasal congestion/obstruction score, loss of smell score and University of Pennsylvania Smell Identification Test score. Disease-specific health-related quality of life (HRQoL) was assessed using the 22-item Sino-Nasal Outcome Test (SNOT-22).
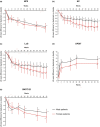
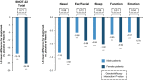
Results: The analysis included 192 male and 111 female patients. Female patients had higher mean SNOT-22 total score (56.6 vs. 49.1, P < 0.01) and more coexisting asthma (78.4% vs. 46.4%, P < 0.0001) and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug-exacerbated respiratory disease (NSAID-ERD) (38.7% vs. 18.8%, P = 0.0001) than male patients, but other baseline characteristics were similar. Dupilumab significantly improved CRSwNP outcomes vs. placebo at Week 52, regardless of gender: least squares mean differences (95% confidence interval) for NPS were -2.33 (-2.80, -1.86) in male and -2.54 (-3.18, -1.90) in female patients (both P < 0.0001 vs. placebo), and for SNOT-22 were -19.2 (-24.1, -14.2) in male and -24.4 (-31.5, -17.3) in female patients (both P < 0.0001 vs. placebo). There were no significant efficacy-by-gender interactions.
Conclusion: Female patients had greater asthma, NSAID-ERD and HRQoL burden at baseline than male patients. Dupilumab treatment significantly improved objective and subjective outcomes compared with placebo, irrespective of gender.
Keywords: chronic rhinosinusitis; health‐related quality of life; patient‐reported outcomes; post hoc analysis.
© 2024 The Authors. Clinical & Translational Immunology published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of Australian and New Zealand Society for Immunology, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
WJF receives research grants from BioInspire Technologies, GlaxoSmithKline, Meda Pharmaceuticals and Sanofi. CB is an advisory board member and receives speakers' fees from ALK, AstraZeneca, GlaxoSmithKline, Mylan, Novartis, Sanofi and Stallergenes Greer. AP, PJR and JAJ‐N are employees and may hold stock and/or stock options in Sanofi. CH is an advisory board member of AstraZeneca, Dianosic, GlaxoSmithKline and Sanofi. OM reports no conflicts of interest. SN, YD and HS are employees and may hold stock and/or stock options in Regeneron Pharmaceuticals Inc.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Dupilumab Improves Outcomes in Patients with Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps and Coexisting Asthma Irrespective of Baseline Asthma Characteristics.J Asthma Allergy. 2023 Apr 18;16:411-419. doi: 10.2147/JAA.S391896. eCollection 2023. J Asthma Allergy. 2023. PMID: 37096015 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and safety of dupilumab in patients with uncontrolled severe chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps and a clinical diagnosis of NSAID-ERD: Results from two randomized placebo-controlled phase 3 trials.Allergy. 2022 Apr;77(4):1231-1244. doi: 10.1111/all.15067. Epub 2021 Oct 1. Allergy. 2022. PMID: 34459002 Free PMC article.
-
Dupilumab improves sense of smell and clinical outcomes in patients with severe chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps with anosmia.Curr Med Res Opin. 2025 Jan;41(1):53-59. doi: 10.1080/03007995.2024.2434083. Epub 2024 Dec 14. Curr Med Res Opin. 2025. Update in: Curr Med Res Opin. 2025 Jan;41(1):ii. doi: 10.1080/03007995.2024.2445962. PMID: 39618256 Updated. Clinical Trial.
-
Biologics for chronic rhinosinusitis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Mar 12;3(3):CD013513. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013513.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 33710614 Free PMC article.
-
Dupilumab: A Review in Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps.Drugs. 2020 May;80(7):711-717. doi: 10.1007/s40265-020-01298-9. Drugs. 2020. PMID: 32240527 Review.
References
-
- Gandhi NA, Pirozzi G, Graham NMH. Commonality of the IL‐4/IL‐13 pathway in atopic diseases. Expert Rev Clin Immunol 2017; 13: 425–437. - PubMed
-
- Bachert CK, Khan AH, Lee SE et al. Prevalence of type 2 inflammatory signatures and efficacy of dupilumab in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps from two phase 3 clinical trials: SINUS‐24 and SINUS‐52. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol 2024; 14: 668–678. - PubMed
-
- Campbell AP, Hoehle LP, Phillips KM, Caradonna DS, Gray ST, Sedaghat AR. Symptom control in chronic rhinosinusitis is an independent predictor of productivity loss. Eur Ann Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Dis 2018; 135: 237–241. - PubMed
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
