Linking IL-6 and hsCRP among Indian patients with myocardial infarction
- PMID: 38854770
- PMCID: PMC11161886
- DOI: 10.6026/973206300200378
Linking IL-6 and hsCRP among Indian patients with myocardial infarction
Abstract
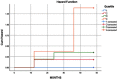
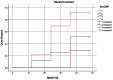
The association between serum interleukin-6 (IL-6) and highly sensitive C - reactive protein (hsCRP) as predictors of the risk factors for Myocardial Infarction. The study included a total of 50 patients with Myocardial Infarction, aged between 25 to 74 years. The levels of hsCRP were measured using the immunoturbidimetry method, while Interleukin 6 was estimated using the sandwich ELISA method. Statistical analysis was conducted using SPSS version 21.0, with p values calculated using Quartile ratio, ANOVA unpaired t-test, and Kaplan-Meier Curve Method. A p-value of less than 0.05 was considered statistically significant. All participants underwent a questionnaire, physical examination, medical history assessment, and laboratory tests. The results of the study showed that there was a significant correlation between IL-6 and hsCRP levels in the Quartile groups, as well as with lipid profiles. The Kaplan-Meier method also demonstrated a significant association between IL-6 and hsCRP levels in participants. The comparison of biomarkers further supported these findings. Thus, data shows that elevated levels of hsCRP and IL-6 could serve as valuable diagnostic markers for predicting Acute Myocardial Infarction. Our study strongly suggests that IL-6 could be a powerful marker in evaluating the Myocardial Infarction.
Keywords: Acute Coronary Syndrome; Biochemical Marker; Interleukin-6; Myocardial infarction; high sensitivity C- reactive protein.
© 2024 Biomedical Informatics.
Figures
Similar articles
-
C-reactive protein and brain natriuretic peptide as predictors of adverse events after lower extremity endovascular revascularization.J Vasc Surg. 2014 Sep;60(3):652-60. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2014.03.254. Epub 2014 Apr 29. J Vasc Surg. 2014. PMID: 24795153 Free PMC article.
-
Does mobilisation of CD34+ stem cells along with VEGF, angiogenin, IL-6, IL-8, and hsCRP levels allow predicting the direction of left ventricular ejection fraction and wall motion score index changes in patients with myocardial infarction?Kardiol Pol. 2013;71(5):464-71. doi: 10.5603/KP.2013.0092. Kardiol Pol. 2013. PMID: 23788086 Clinical Trial.
-
Relationship between high sensitivity C-reactive protein and angiographic severity of coronary artery disease.J Geriatr Cardiol. 2020 May;17(5):256-263. doi: 10.11909/j.issn.1671-5411.2020.05.003. J Geriatr Cardiol. 2020. PMID: 32547608 Free PMC article.
-
From C-Reactive Protein to Interleukin-6 to Interleukin-1: Moving Upstream To Identify Novel Targets for Atheroprotection.Circ Res. 2016 Jan 8;118(1):145-56. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.115.306656. Circ Res. 2016. PMID: 26837745 Free PMC article. Review.
-
High sensitivity C-reactive protein in cardiovascular risk assessment. CRP mania or useful screening?Int Angiol. 2003 Mar;22(1):15-23. Int Angiol. 2003. PMID: 12771851 Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
