Factors influencing telemedicine adoption among physicians in the Malaysian healthcare system: A revisit
- PMID: 38854922
- PMCID: PMC11159542
- DOI: 10.1177/20552076241257050
Factors influencing telemedicine adoption among physicians in the Malaysian healthcare system: A revisit
Abstract
Background: The Malaysian healthcare system is under strain due to an aging population, the rising prevalence of chronic diseases, and heavy workloads among physicians. As costs and requirements continue to rise, telemedicine is critical for bridging gaps in supply and demand. However, there are limited studies on telemedicine adoption among Malaysian physicians. Furthermore, the existing literature on telemedicine adoption does not contain a comprehensive framework that integrates the multidimensional social influence, and technological, clinical, and individual factors.
Objective: This research investigates the adoption of telemedicine among Malaysian physicians. It draws from the Technology Acceptance Model (TAM) and Kelman's Social Influence Theory.
Methods: A survey was conducted among 230 participants in hospitals located in Kuala Lumpur and Selangor. The data were analyzed using Partial Least Squares Structural Equation Modeling (PLS-SEM).
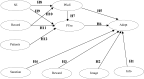
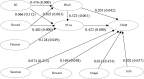
Results: The study identified crucial factors influencing telemedicine adoption, including informational influences, rewards, perceived ease of use, and usefulness. Meanwhile, the Importance-performance Map Analysis (IPMA) identified perceived ease of use as the most important factor for physicians, but the highest performance was patient's records.
Conclusions: The proposed integrated model enhances the understanding of telemedicine adoption and highlights the differential effects of individual, technological, clinical, and multidimensional social influence factors from the physicians' perspective. The findings can guide future studies and influence implementation strategies for telemedicine promotion in the Malaysian healthcare context. Hospitals should prioritize user-friendly technology and information provision, while telemedicine providers should enhance the accessibility of patient records to facilitate telemedicine adoption. Policymakers should consider supporting training programs that will boost physicians' confidence in effectively utilizing telemedicine.
Keywords: Malaysia; TAM; Telemedicine; adoption; behavior; physicians; quantitative; social influence theory.
© The Author(s) 2024.
Conflict of interest statement
The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Determinants of Telehealth Adoption Among Older Adults: Cross-Sectional Survey Study.JMIR Aging. 2025 Mar 24;8:e60936. doi: 10.2196/60936. JMIR Aging. 2025. PMID: 40126531 Free PMC article.
-
Investigating Physicians' Adoption of Telemedicine in Romania Using Technology Acceptance Model (TAM).Healthcare (Basel). 2024 Aug 1;12(15):1531. doi: 10.3390/healthcare12151531. Healthcare (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39120234 Free PMC article.
-
Modeling telemedicine continuance usage: findings from PLS-SEM and fsQCA.J Health Organ Manag. 2025 Feb 14. doi: 10.1108/JHOM-09-2024-0376. Online ahead of print. J Health Organ Manag. 2025. PMID: 39934985
-
Healthcare stakeholders' perceptions and experiences of factors affecting the implementation of critical care telemedicine (CCT): qualitative evidence synthesis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Feb 18;2(2):CD012876. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012876.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 33599282 Free PMC article.
-
Understanding Clinicians' Adoption of Mobile Health Tools: A Qualitative Review of the Most Used Frameworks.JMIR Mhealth Uhealth. 2020 Jul 6;8(7):e18072. doi: 10.2196/18072. JMIR Mhealth Uhealth. 2020. PMID: 32442132 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Determinants of Telehealth Adoption Among Older Adults: Cross-Sectional Survey Study.JMIR Aging. 2025 Mar 24;8:e60936. doi: 10.2196/60936. JMIR Aging. 2025. PMID: 40126531 Free PMC article.
-
The Sri Lankan enigma: demystifying public healthcare information systems acceptance.BMC Health Serv Res. 2025 Jan 4;25(1):24. doi: 10.1186/s12913-024-12173-8. BMC Health Serv Res. 2025. PMID: 39755700 Free PMC article.
-
Implementation of a tele-paediatric network in hospitals in a rural region: A mixed methods implementation study.Digit Health. 2025 Jul 20;11:20552076251350924. doi: 10.1177/20552076251350924. eCollection 2025 Jan-Dec. Digit Health. 2025. PMID: 40693249 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ong AKS, Kurata YB, Castro SADG, et al. Factors influencing the acceptance of telemedicine in the Philippines. Technol Soc 2022; 70: 102040.
-
- WHO. Global spending on health: rising to the pandemic’s challenges, https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/365133 (2022).
-
- ATA. Telehealth basics, https://www.americantelemed.org/resource/why-telemedicine/.
-
- Pylypchuk Y, Barker W. Use of Telemedicine among Office-Based Physicians, 2021. Washington: DC: ONC Data Brief, no. 65. Office of the National Coordinator for Health Information Technology, 2023.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials