Outcomes of initial therapy for synchronous brain metastases from small cell lung cancer: a single-institution retrospective analysis
- PMID: 38854935
- PMCID: PMC11157380
- DOI: 10.21037/tlcr-23-641
Outcomes of initial therapy for synchronous brain metastases from small cell lung cancer: a single-institution retrospective analysis
Abstract
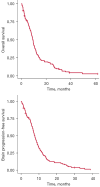
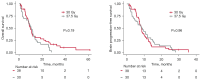
Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) has a propensity for brain metastases, which is associated with poor prognosis. We sought to determine predictors of overall survival (OS) and brain progression-free survival (bPFS) in SCLC patients with synchronous brain metastases at the time of initial SCLC diagnosis. A total of 107 SCLC patients with synchronous brain metastases treated at a single institution were included in this retrospective analysis. These patients had brain lesions present on initial staging imaging. Survival was estimated using the Kaplan-Meier method with log-rank test. Factors predictive of OS and bPFS were analyzed using Cox proportional hazards regression model. Median OS for the entire cohort was 9 months (interquartile range, 4.2-13.8 months) and median bPFS was 7.3 months (interquartile range, 3.5-11.1 months). OS was 30.3% at 1 year and 14.4% at 2 years, while bPFS was 22.0% at 1 year and 6.9% at 2 years. The median number of brain lesions at diagnosis was 3 (interquartile range, 2-8), and the median size of the largest metastasis was 2.0 cm (interquartile range, 1.0-3.3 cm). Increased number of brain lesions was significantly associated with decreased OS. Patients who received both chemotherapy and whole brain radiation therapy (WBRT) had improved OS (P=0.02) and bPFS (P=0.005) compared to those who had either chemotherapy or WBRT alone. There was no significant difference in OS or bPFS depending on the sequence of therapy or the dose of WBRT. Thirteen patients underwent upfront brain metastasis resection, which was associated with improved OS (P=0.02) but not bPFS (P=0.09) compared to those who did not have surgery. The combination of chemotherapy and WBRT was associated with improved OS and bPFS compared to either modality alone. Upfront brain metastasis resection was associated with improved OS but not bPFS compared to those who did not have surgery.
Keywords: Small cell lung cancer (SCLC); brain metastases; chemotherapy; craniotomy; radiation therapy.
2024 Translational Lung Cancer Research. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://tlcr.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/tlcr-23-641/coif). T.R.H. reports receiving consulting fees from Medtronics which is not relevant to the work in this paper. T.B. reports funding from National Cancer Institute (NCI) Cancer Therapy Evaluation Program (CTEP) as national principle investigator (PI) of a clinical trial 04/22-3/23, which is not relevant to this study. A.D. reports participation in data safety monitoring board or advisory board on Ipsen, Amgen, Jazz, BMS, Astra Zeneca. S.C. reports receiving funding from the National Institutes of Health 01/20-11/23 (grant No. K12CA076917 to S.C. for salary support and research funds); participation in advisory boards for Telix Pharmaceuticals, Seagen Inc. and GT Medical. A.E.S. reports funding from U01 CS236215 06/19-5/23 (PI: Sloan), R01 CA 217956 06/17-05/22 (PI: Brady-Kalnay), R21 CA256573 01/21-12/22 (PI: Sloan), P01 CA CA245705-01 09/20-08/25 (PI: Lathia), Merck Case 3316 12/17-11/21 (PI: Sloan), Coulter Translational Research Fund 09/17-08/22 (PI: Brady-Kalnay), Jobs Ohio 5/22-11/23 (PI: Brady-Kalnay); options for <1% of company shares of Surgical Theater; consulting fees from Medtronic (Visualase), Monteris Medical Inc. and Surgical Theater; patents on the usage of PS-Binding CAR-T Cells and the procoagulant function of cancer stem cells. The other authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Outcome and prognostic factors in single brain metastases from small-cell lung cancer.Strahlenther Onkol. 2018 Feb;194(2):98-106. doi: 10.1007/s00066-017-1228-4. Epub 2017 Oct 30. Strahlenther Onkol. 2018. PMID: 29085978 English.
-
Outcome and prognostic factors in patients with brain metastases from small-cell lung cancer treated with whole brain radiotherapy.J Neurooncol. 2017 Aug;134(1):205-212. doi: 10.1007/s11060-017-2510-0. Epub 2017 May 30. J Neurooncol. 2017. PMID: 28560661
-
Optimizing Whole Brain Radiotherapy Treatment and Dose for Patients With Brain Metastases From Small Cell Lung Cancer.Front Oncol. 2021 Oct 25;11:726613. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.726613. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34760692 Free PMC article.
-
Additional radiation boost to whole brain radiation therapy may improve the survival of patients with brain metastases in small cell lung cancer.Radiat Oncol. 2018 Dec 18;13(1):250. doi: 10.1186/s13014-018-1198-4. Radiat Oncol. 2018. PMID: 30563554 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Brain metastases from epithelial ovarian cancer. The Hellenic Cooperative Oncology Group (HeCOG) experience and review of the literature.Anticancer Res. 2005 Sep-Oct;25(5):3553-8. Anticancer Res. 2005. PMID: 16101179 Review.
Cited by
-
Evaluating the efficacy and safety of Anlotinib in conjunction with stereotactic radiosurgery for small cell lung cancer patients with brain metastases.Oncol Res. 2025 Mar 19;33(4):885-894. doi: 10.32604/or.2024.051586. eCollection 2025. Oncol Res. 2025. PMID: 40191725 Free PMC article.
-
External Validation of an Extended Prognostic Assessment Model in Patients With Brain Metastases from Small-cell Lung Cancer.Cancer Diagn Progn. 2025 Mar 3;5(2):171-178. doi: 10.21873/cdp.10427. eCollection 2025 Mar-Apr. Cancer Diagn Progn. 2025. PMID: 40034954 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
