Potential predictors of the pathologic response after neoadjuvant chemoimmunotherapy in resectable non-small cell lung cancer: a narrative review
- PMID: 38854945
- PMCID: PMC11157365
- DOI: 10.21037/tlcr-24-142
Potential predictors of the pathologic response after neoadjuvant chemoimmunotherapy in resectable non-small cell lung cancer: a narrative review
Abstract
Background and objective: Neoadjuvant chemoimmunotherapy (NACI) is the standard of care for patients with resectable non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Although the pathological complete response (pCR) after NACI reportedly exceeds 20%, an optimal predictor of pCR is yet to be established. This review aims to examine the possible predictors of pCR after NACI.
Methods: We identified research article published between 2018 and 2022 in English by the PubMed database. Fifty research studies were considered as relevant article, and were examined to edit information for this narrative review.
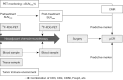
Key content and findings: Recently, several studies have explored potential biomarkers for the pathological response after NACI. For example, 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography (18F-FDG-PET) imaging, tumor microenvironment (TME), genetic alternation such as circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA), and clinical markers such as neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) and smoking signature were assessed in patients with resectable NSCLC to predict the pathological response after NACI. Based on the PET response criteria, the complete metabolic response (CMR) achieved a positive predictive value (PPV) of 71.4% for predicting pCR, and the decreasing rate of post-therapy maximum standardized uptake value (SUVmax) after NACI substantially correlated with the major pathological response (MPR). TME, as a significant marker for MPR in tumor specimens, was identified as an increase in CD8+ T cells and decrease in CD3+ T cells or Foxp3 T cells. Considering blood samples, TME comprised an increase in CD4+PD-1+ cells or natural killer cells and a decrease in CD3+CD56+CTLA4+ cells, total T cells, Th cells, myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs), or regulatory T cells. Although low pretreatment levels of ctDNA and undetectable ctDNA levels after NACI were markedly associated with survival, the relationship between ctDNA levels and pCR remains elusive. Moreover, the patients with a high baseline NLR had a low incidence of pCR. Heavy smoking (>40 pack-years) was favorable for predicting pathological response.
Conclusions: A reduced rate of 18F-FDG uptake post-NACI and TME-related surface markers on lymphocytes could be optimal predictors for pCR. However, the role of these pCR predictors for NACI remains poorly validated, warranting further investigations. This review focuses on predictive biomarkers for pathological response after NACI in patients with resectable NSCLC.
Keywords: Pathological complete response (pCR); lung cancer; neoadjuvant chemoimmunotherapy (NACI); predictive marker.
2024 Translational Lung Cancer Research. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://tlcr.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/tlcr-24-142/coif). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials