Late-Onset Ataxia-Telangiectasia Presenting With Dystonia and Tremor: The Use of Nanopore Long-Read Sequencing Solving the Variant Phase
- PMID: 38854973
- PMCID: PMC11157422
- DOI: 10.1212/NXG.0000000000200141
Late-Onset Ataxia-Telangiectasia Presenting With Dystonia and Tremor: The Use of Nanopore Long-Read Sequencing Solving the Variant Phase
Abstract
Objectives: This study investigates atypical late-onset ataxia-telangiectasia (AT) cases in a Korean family, diagnosed via Nanopore long-read sequencing, diverging from the typical early childhood onset caused by biallelic pathogenic ATM variants.
Methods: A 52-year-old Korean woman exhibiting dystonia and tremor, with a family history of similar symptoms in her older sister, underwent comprehensive tests including routine laboratory tests, neuropsychological assessments, and neuroimaging. Genetic analysis was conducted through targeted sequencing of 29 dystonia-associated genes and Nanopore long-read sequencing to assess the configuration of 2 ATM gene variants.
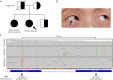
Results: Routine blood tests and brain imaging studies returned normal results, except for elevated α-fetoprotein levels. Neurologic examination revealed dystonia in the face, hand, and trunk, along with cervical dystonia in the proband. Her sister exhibited similar symptoms without evident telangiectasia. Genetic testing revealed 2 heterozygous pathogenic ATM gene variants (p.Glu2014Ter and p.Glu2052Lys). Nanopore long-read sequencing confirmed these variants were in trans configuration, establishing a definite molecular diagnosis in the proband.
Discussion: This report expands the known clinical spectrum of AT, highlighting a familial case of atypical AT. Moreover, it underscores the clinical utility of Nanopore long-read sequencing in phasing variant haplotypes, essential for diagnosing autosomal recessive disorders, especially beneficial for cases without parental samples.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. on behalf of the American Academy of Neurology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no relevant disclosures. Go to Neurology.org/NG for full disclosures.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
