C176-loaded and phosphatidylserine-modified nanoparticles treat retinal neovascularization by promoting M2 macrophage polarization
- PMID: 38855060
- PMCID: PMC11157223
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2024.05.038
C176-loaded and phosphatidylserine-modified nanoparticles treat retinal neovascularization by promoting M2 macrophage polarization
Abstract
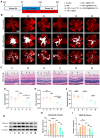
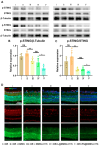
Retinal neovascularization (RNV), a typical pathological manifestation involved in most neovascular diseases, causes retinal detachment, vision loss, and ultimately irreversible blindness. Repeated intravitreal injections of anti-VEGF drugs were developed against RNV, with limitations of incomplete responses and adverse effects. Therefore, a new treatment with a better curative effect and more prolonged dosage is demanding. Here, we induced macrophage polarization to anti-inflammatory M2 phenotype by inhibiting cGAS-STING signaling with an antagonist C176, appreciating the role of cGAS-STING signaling in the retina in pro-inflammatory M1 polarization. C176-loaded and phosphatidylserine-modified dendritic mesoporous silica nanoparticles were constructed and examined by a single intravitreal injection. The biosafe nanoparticles were phagocytosed by retinal macrophages through a phosphatidylserine-mediated "eat me" signal, which persistently release C176 to suppress STING signaling and thereby promote macrophage M2 polarization specifically. A single dosage can effectively alleviate pathological angiogenesis phenotypes in murine oxygen-induced retinopathy models. In conclusion, these C176-loaded nanoparticles with enhanced cell uptake and long-lasting STING inhibition effects might serve as a promising way for treating RNV.
Keywords: Macrophage polarization; Nanocarrier; Retinal neovascularization; cGAS-STING pathway.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures






References
-
- Wong T.Y., Cheung C.M.G., Larsen M., Sharma S., Simó R. Diabetic retinopathy. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2016 Mar;2 - PubMed
-
- Cheung N., Mitchell P., Wong T.Y. Diabetic retinopathy. Lancet. 2010;376(9735):124–136. - PubMed
-
- Li X., Xu G., Wang Y., Xu X., Liu X., Tang S., et al. Safety and efficacy of conbercept in neovascular age-related macular degeneration: results from a 12-month randomized phase 2 Study: AURORA study. Ophthalmology. 2014;121(9):1740–1747. - PubMed
-
- Heier J.S., Brown D.M., Chong V., Korobelnik J.F., Kaiser P.K., Nguyen Q.D., et al. Intravitreal aflibercept (VEGF trap-eye) in wet age-related macular degeneration. Ophthalmology. 2012 Dec;119(12):2537–2548. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

