Interleukin-1 regulates follicular T cells during the germinal center reaction
- PMID: 38855101
- PMCID: PMC11157057
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1393096
Interleukin-1 regulates follicular T cells during the germinal center reaction
Abstract
Introduction: Antibody production and the generation of memory B cells are regulated by T follicular helper (Tfh) and T follicular regulatory (Tfr) cells in germinal centers. However, the precise role of Tfr cells in controlling antibody production is still unclear. We have previously shown that both Tfh and Tfr cells express the IL-1R1 agonist receptor, whereas only Tfr cells express the IL-1R2 decoy and IL-1Ra antagonist receptors. We aimed to investigate the role of IL-1 receptors in the regulation of B cell responses by Tfh and Tfr.
Methods: We generated mice with IL-1 receptors inactivated in Tfh or Tfr and measured antibody production and cell activation after immunisation.
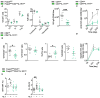
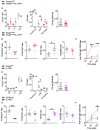
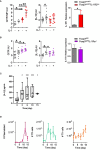
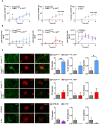
Results: While IL-1β levels are increased in the draining lymph node after immunisation, antigen-specific antibody levels and cell phenotypes indicated that IL-1β can activate both Tfh and Tfr cells through IL-1R1 stimulation. Surprisingly, expression of IL-1R2 and IL-1Ra on Tfr cells does not block IL-1 activation of Tfh cells, but rather prevents IL-1/IL-1R1-mediated early activation of Tfr cells. IL-1Rs also regulate the antibody response to autoantigens and its associated pathophysiology in an experimental lupus model.
Discussion: Collectively, our results show that IL-1 inhibitory receptors expressed by Tfr cells prevent their own activation and suppressive function, thus licensing IL-1-mediated activation of Tfh cells after immunisation. Further mechanistic studies should unravel these complex interactions between IL-1β and follicular helper and regulatory T cells and provide new avenues for therapeutic intervention.
Keywords: adaptive immunity; autoimmune diseases; humoral response; immunotherapy; vaccination.
Copyright © 2024 Belbezier, Engeroff, Fourcade, Vantomme, Vaineau, Gouritin, Bellier, Brocheriou, Tchitchek, Graff-Dubois and Klatzmann.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
IL-1β signaling modulates T follicular helper and regulatory cells in human lymphoid tissues.JCI Insight. 2025 May 20;10(12):e188724. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.188724. eCollection 2025 Jun 23. JCI Insight. 2025. PMID: 40392614 Free PMC article.
-
IL-21 Receptor Blockade Shifts the Follicular T Cell Balance and Reduces De Novo Donor-Specific Antibody Generation.Front Immunol. 2021 Apr 9;12:661580. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.661580. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33897706 Free PMC article.
-
Dysregulated TFR and TFH cells correlate with B-cell differentiation and antibody production in autoimmune hepatitis.J Cell Mol Med. 2020 Apr;24(7):3948-3957. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.14997. Epub 2020 Mar 6. J Cell Mol Med. 2020. PMID: 32142205 Free PMC article.
-
Frontiers of Autoantibodies in Autoimmune Disorders: Crosstalk Between Tfh/Tfr and Regulatory B Cells.Front Immunol. 2021 Mar 26;12:641013. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.641013. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33841422 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Control of foreign Ag-specific Ab responses by Treg and Tfr.Immunol Rev. 2020 Jul;296(1):104-119. doi: 10.1111/imr.12888. Epub 2020 Jun 20. Immunol Rev. 2020. PMID: 32564426 Review.
Cited by
-
IL-1β signaling modulates T follicular helper and regulatory cells in human lymphoid tissues.JCI Insight. 2025 May 20;10(12):e188724. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.188724. eCollection 2025 Jun 23. JCI Insight. 2025. PMID: 40392614 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cohen I, Rider P, Carmi Y, Braiman A, Dotan S, White MR, et al. . Differential release of chromatin-bound IL-1α discriminates between necrotic and apoptotic cell death by the ability to induce sterile inflammation. Proc Natl Acad Sci. (2010) 107:2574–9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0915018107 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

