Integrative analysis of COL6A3 in lupus nephritis: insights from single-cell transcriptomics and proteomics
- PMID: 38855105
- PMCID: PMC11157080
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1309447
Integrative analysis of COL6A3 in lupus nephritis: insights from single-cell transcriptomics and proteomics
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum: Integrative analysis of COL6A3 in lupus nephritis: insights from single-cell transcriptomics and proteomics.Front Immunol. 2024 Oct 21;15:1508292. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1508292. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39497818 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Introduction: Lupus nephritis (LN), a severe complication of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), presents significant challenges in patient management and treatment outcomes. The identification of novel LN-related biomarkers and therapeutic targets is critical to enhancing treatment outcomes and prognosis for patients.
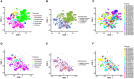
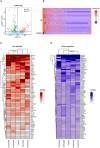
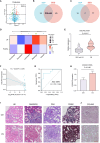
Methods: In this study, we analyzed single-cell expression data from LN (n=21) and healthy controls (n=3). A total of 143 differentially expressed genes were identified between the LN and control groups. Then, proteomics analysis of LN patients (n=9) and control (SLE patients without LN, n=11) revealed 55 differentially expressed genes among patients with LN and control group. We further utilizes protein-protein interaction network and functional enrichment analyses to elucidate the pivotal role of COL6A3 in key signaling pathways. Its diagnostic value is evaluate through its correlation with disease progression and renal function metrics, as well as Receiver Operating Characteristic Curve (ROC) analysis. Additionally, immunohistochemistry and qPCR experiments were performed to validate the expression of COL6A3 in LN.
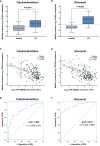
Results: By comparison of single-cell and proteomics data, we discovered that COL6A3 is significantly upregulated, highlighting it as a critical biomarker of LN. Our findings emphasize the substantial involvement of COL6A3 in the pathogenesis of LN, particularly noting its expression in mesangial cells. Through comprehensive protein-protein interaction network and functional enrichment analyses, we uncovered the pivotal role of COL6A3 in key signaling pathways including integrin-mediated signaling pathways, collagen-activated signaling pathways, and ECM-receptor interaction, suggesting potential therapeutic targets. The diagnostic utility is confirmed by its correlation with disease progression and renal function metrics of the glomerular filtration rate. ROC analysis further validates the diagnostic value of COL6A3, with the area under the ROC values of 0.879 in the in-house cohort, and 0.802 and 0.915 in tubular and glomerular external cohort samples, respectively. Furthermore, immunohistochemistry and qPCR experiments were consistent with those obtained from the single-cell RNA sequencing and proteomics studies.
Discussion: These results proved that COL6A3 is a promising biomarker and therapeutic target, advancing personalized medicine strategies for LN.
Keywords: COL6A3; biomarkers; diagnosis; kidney disease; lupus nephritis; proteomics; single-cell RNA sequencing; systemic lupus erythematosus.
Copyright © 2024 Mou, Zhang, Liu, Lu, Yue, Lai, Pu, Huang and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
LncRNA XIST/miR-381-3P/STAT1 axis as a potential biomarker for lupus nephritis.Lupus. 2024 Oct;33(11):1176-1191. doi: 10.1177/09612033241273072. Epub 2024 Aug 9. Lupus. 2024. PMID: 39126180
-
Systematic identification of key extracellular proteins as the potential biomarkers in lupus nephritis.Front Immunol. 2022 Jul 28;13:915784. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.915784. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35967373 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of serum exosomal miRNA biomarkers in patients with lupus nephritis.Clin Rheumatol. 2025 Jun;44(6):2299-2310. doi: 10.1007/s10067-025-07447-3. Epub 2025 May 3. Clin Rheumatol. 2025. PMID: 40319190
-
Biomarker profiling for lupus nephritis.Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics. 2013 Jun;11(3):158-65. doi: 10.1016/j.gpb.2013.05.003. Epub 2013 Jun 1. Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics. 2013. PMID: 23732627 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus with a Focus on Lupus Nephritis.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jun 3;25(11):6162. doi: 10.3390/ijms25116162. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38892349 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Diversity and heterogeneity in human pancreaticobiliary maljunction revealed by single-cell RNA sequencing.Pediatr Surg Int. 2025 Mar 21;41(1):98. doi: 10.1007/s00383-025-05997-w. Pediatr Surg Int. 2025. PMID: 40116982
-
Multi-omics approaches for biomarker discovery and precision diagnosis of prediabetes.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025 Mar 14;16:1520436. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1520436. eCollection 2025. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40162315 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Integrating genomics and AI to uncover molecular targets for mRNA vaccine development in lupus nephritis.Front Immunol. 2024 Oct 4;15:1381445. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1381445. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39430760 Free PMC article.
-
Circulatory microRNAs and proinflammatory cytokines as predictors of lupus nephritis.Front Immunol. 2024 Oct 11;15:1449296. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1449296. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39464895 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fanouriakis A, Kostopoulou M, Cheema K, Anders H-J, Aringer M, Bajema I, et al. . 2019 Update of the Joint European League Against Rheumatism and European Renal Association-European Dialysis and Transplant Association (EULAR/ERA-EDTA) recommendations for the management of lupus nephritis. Ann Rheum Dis. (2020) 79:713–23. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2020-216924 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

