Latest insights into the global epidemiological features, screening, early diagnosis and prognosis prediction of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
- PMID: 38855150
- PMCID: PMC11154680
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i20.2638
Latest insights into the global epidemiological features, screening, early diagnosis and prognosis prediction of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
Abstract
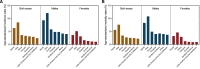
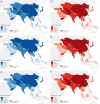
As a highly invasive carcinoma, esophageal cancer (EC) was the eighth most prevalent malignancy and the sixth leading cause of cancer-related death worldwide in 2020. Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) is the major histological subtype of EC, and its incidence and mortality rates are decreasing globally. Due to the lack of specific early symptoms, ESCC patients are usually diagnosed with advanced-stage disease with a poor prognosis, and the incidence and mortality rates are still high in many countries, especially in China. Therefore, enormous challenges still exist in the management of ESCC, and novel strategies are urgently needed to further decrease the incidence and mortality rates of ESCC. Although the key molecular mechanisms underlying ESCC pathogenesis have not been fully elucidated, certain promising biomarkers are being investigated to facilitate clinical decision-making. With the advent and advancement of high-throughput technologies, such as genomics, proteomics and metabolomics, valuable biomarkers with high sensitivity, specificity and stability could be identified for ESCC. Herein, we aimed to determine the epidemiological features of ESCC in different regions of the world, especially in China, and focused on novel molecular biomarkers associated with ESCC screening, early diagnosis and prognosis prediction.
Keywords: Diagnosis; Epidemiology; Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma; Genomics; Metabolomics; Proteomics.
©The Author(s) 2024. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: All the authors report no relevant conflicts of interest for this article.
Figures


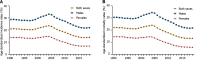
References
-
- Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, Bray F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71:209–249. - PubMed
-
- Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, Zhang S, Zeng H, Bray F, Jemal A, Yu XQ, He J. Cancer statistics in China, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 2016;66:115–132. - PubMed
-
- Baba Y, Yoshida N, Kinoshita K, Iwatsuki M, Yamashita YI, Chikamoto A, Watanabe M, Baba H. Clinical and Prognostic Features of Patients With Esophageal Cancer and Multiple Primary Cancers: A Retrospective Single-institution Study. Ann Surg. 2018;267:478–483. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

