Hydrogen-rich water alleviates constipation by attenuating oxidative stress through the sirtuin1/nuclear factor-erythroid-2-related factor 2/heme oxygenase-1 signaling pathway
- PMID: 38855154
- PMCID: PMC11154682
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i20.2709
Hydrogen-rich water alleviates constipation by attenuating oxidative stress through the sirtuin1/nuclear factor-erythroid-2-related factor 2/heme oxygenase-1 signaling pathway
Abstract
Background: Constipation, a highly prevalent functional gastrointestinal disorder, induces a significant burden on the quality of patients' life and is associated with substantial healthcare expenditures. Therefore, identifying efficient therapeutic modalities for constipation is of paramount importance. Oxidative stress is a pivotal contributor to colonic dysmotility and is the underlying pathology responsible for constipation symptoms. Consequently, we postulate that hydrogen therapy, an emerging and promising intervention, can serve as a safe and efficacious treatment for constipation.
Aim: To determine whether hydrogen-rich water (HRW) alleviates constipation and its potential mechanism.
Methods: Constipation models were established by orally loperamide to Sprague-Dawley rats. Rats freely consumed HRW, and were recorded their 24 h total stool weight, fecal water content, and charcoal propulsion rate. Fecal samples were subjected to 16S rDNA gene sequencing. Serum non-targeted metabolomic analysis, malondialdehyde, and superoxide dismutase levels were determined. Colonic tissues were stained with hematoxylin and eosin, Alcian blue-periodic acid-Schiff, reactive oxygen species (ROS) immunofluorescence, and immunohistochemistry for cell growth factor receptor kit (c-kit), PGP 9.5, sirtuin1 (SIRT1), nuclear factor-erythroid-2-related factor 2 (Nrf2), and heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1). Quantitative real-time PCR and western blot analysis were conducted to determine the expression level of SIRT1, Nrf2 and HO-1. A rescue experiment was conducted by intraperitoneally injecting the SIRT1 inhibitor, EX527, into constipated rats. NCM460 cells were induced with H2O2 and treated with the metabolites to evaluate ROS and SIRT1 expression.
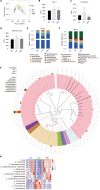
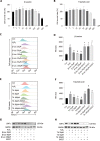
Results: HRW alleviated constipation symptoms by improving the total amount of stool over 24 h, fecal water content, charcoal propulsion rate, thickness of the intestinal mucus layer, c-kit expression, and the number of intestinal neurons. HRW modulated intestinal microbiota imbalance and abnormalities in serum metabolism. HRW could also reduce intestinal oxidative stress through the SIRT1/Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway. This regulatory effect on oxidative stress was confirmed via an intraperitoneal injection of a SIRT1 inhibitor to constipated rats. The serum metabolites, β-leucine (β-Leu) and traumatic acid, were also found to attenuate H2O2-induced oxidative stress in NCM460 cells by up-regulating SIRT1.
Conclusion: HRW attenuates constipation-associated intestinal oxidative stress via SIRT1/Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway, modulating gut microbiota and serum metabolites. β-Leu and traumatic acid are potential metabolites that upregulate SIRT1 expression and reduce oxidative stress.
Keywords: Constipation; Gut microbiota; Hydrogen-rich water; Oxidative stress; Serum metabolites; Sirtuin1.
©The Author(s) 2024. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: All the authors report no relevant conflicts of interest for this article.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Zhongfeng Xingnao Liquid ameliorates post-stroke cognitive impairment through sirtuin1 (SIRT1)/nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2)/heme oxygenase 1 (HO-1) pathway.Chin J Nat Med. 2025 Jan;23(1):77-89. doi: 10.1016/S1875-5364(25)60808-9. Chin J Nat Med. 2025. PMID: 39855833
-
[Role and mechanism of SIRT1 in regulating Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway in septic liver injury].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2023 Jun;35(6):598-603. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn121430-20220815-00744. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2023. PMID: 37366125 Chinese.
-
Zuogui Pills alleviate cyclophosphamide-induced ovarian aging by reducing oxidative stress and restoring the stemness of oogonial stem cells through the Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway.J Ethnopharmacol. 2024 Oct 28;333:118505. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2024.118505. Epub 2024 Jun 28. J Ethnopharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38945466
-
The SIRT-1/Nrf2/HO-1 axis: Guardians of neuronal health in neurological disorders.Behav Brain Res. 2025 Jan 5;476:115280. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2024.115280. Epub 2024 Oct 4. Behav Brain Res. 2025. PMID: 39368713 Review.
-
Functional Food Nutrients, Redox Resilience Signaling and Neurosteroids for Brain Health.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Nov 12;25(22):12155. doi: 10.3390/ijms252212155. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39596221 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Naringenin attenuates slow-transit constipation by regulating the AMPK/mTOR/ULK1 signalling pathway: in vivo and in vitro studies.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Jun 17;16:1550458. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1550458. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40599805 Free PMC article.
-
Role and mechanism of molecular hydrogen in the treatment of Parkinson's diseases.Front Neurosci. 2025 Apr 23;19:1576773. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2025.1576773. eCollection 2025. Front Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 40336538 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Runchangningshen paste activates NLRP6 inflammasome-mediated autophagy to stimulate colonic mucin-2 secretion and modulates mucosal microbiota in functional constipation.World J Gastroenterol. 2025 Mar 7;31(9):102256. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i9.102256. World J Gastroenterol. 2025. PMID: 40061589 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Hydrogen Therapy: Mechanisms, Delivery Methods, Preventive, and Therapeutic Application.MedComm (2020). 2025 Apr 28;6(5):e70194. doi: 10.1002/mco2.70194. eCollection 2025 May. MedComm (2020). 2025. PMID: 40297245 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Unveiling Xuanshen decoction: A novel approach to combat slow transit constipation.World J Gastroenterol. 2025 Aug 14;31(30):109187. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i30.109187. World J Gastroenterol. 2025. PMID: 40904888 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Black CJ, Drossman DA, Talley NJ, Ruddy J, Ford AC. Functional gastrointestinal disorders: advances in understanding and management. Lancet. 2020;396:1664–1674. - PubMed
-
- Sayuk GS, Waldman SA, Brenner DM. Mechanisms of Action of Current Pharmacologic Options for the Treatment of Chronic Idiopathic Constipation and Irritable Bowel Syndrome With Constipation. Am J Gastroenterol. 2022;117:S6–S13. - PubMed
-
- Zhou G, Goshi E, He Q. Micro/Nanomaterials-Augmented Hydrogen Therapy. Adv Healthc Mater. 2019;8:e1900463. - PubMed
-
- Ohsawa I, Ishikawa M, Takahashi K, Watanabe M, Nishimaki K, Yamagata K, Katsura K, Katayama Y, Asoh S, Ohta S. Hydrogen acts as a therapeutic antioxidant by selectively reducing cytotoxic oxygen radicals. Nat Med. 2007;13:688–694. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

