The Clinical Value of the Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio, the C-Reactive Protein-to-Albumin Ratio, the Systemic Inflammatory Index, and the Systemic Inflammatory Response Index in Patients with the Anti-Synthetase Syndrome
- PMID: 38855168
- PMCID: PMC11162194
- DOI: 10.2147/JIR.S460610
The Clinical Value of the Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio, the C-Reactive Protein-to-Albumin Ratio, the Systemic Inflammatory Index, and the Systemic Inflammatory Response Index in Patients with the Anti-Synthetase Syndrome
Abstract
Objective: There are no studies examining the role of the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR), the C-reactive protein-to-albumin ratio (CAR), the systemic inflammatory index (SII), and the systemic inflammatory response index (SIRI) in anti-synthetase syndrome (ASS). We aim to compare NLR, CAR, SII, and SIRI in ASS and dermatomyositis/polymyositis (DM/PM), as well as to examine potential correlations between NLR, CAR, SII, and SIRI and clinical features and laboratory parameters in ASS.
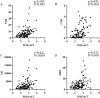
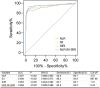
Methods: Retrospective collection of data from 111 patients with ASS and 175 patients with DM/PM. A Spearman rank correlation analysis was utilized to analyze the correlation between NLR, CAR, SII, and SIRI and inflammatory indexes. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves were used to assess the diagnostic value. Univariate logistic regression analysis was performed to assess risk factors for interstitial lung disease (ILD).
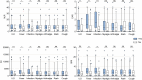
Results: Compared with DM/PM, NLR, CAR, SII, and SIRI were significantly greater in ASS patients (p < 0.05). NLR, CAR, SII, and SIRI were correlated with albumin, lactic dehydrogenase (LDH), C-reactive protein (CRP), ferritin, white blood cell (WBC), platelets, and myositis disease activity assessment visual analog scales (MYOACT) score (p < 0.05). The ROC curves analysis showed that NLR, SII, and SIRI were all highly predictive of the occurrence of ASS. Comparisons based on clinical characteristics showed elevated levels of NLR, CAR, SII, and SIRI in ASS patients with ILD, fever, and infection (p < 0.05). Univariate logistic regression analysis revealed that NLR, CAR, and SII were significant risk factors for ASS-ILD (p < 0.05).
Conclusion: The levels of NLR, CAR, SII, and SIRI were higher in ASS than in DM/PM and correlated with disease activity and specific clinical features. NLR, CAR, SII, and SIRI may be an aid in differentiating ASS from DM/PM and maybe promising biomarkers for ASS.
Keywords: anti-synthase syndrome; the C-reactive protein-to-albumin ratio; the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio; the systemic immune inflammation index; the systemic inflammation response index.
© 2024 Huang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The predictive role of composite inflammatory ratio parameters in the conscious awareness recovery after severe acute ischemic stroke: a retrospective cohort study.BMC Neurol. 2025 Mar 6;25(1):90. doi: 10.1186/s12883-024-04016-0. BMC Neurol. 2025. PMID: 40050808 Free PMC article.
-
Association of systemic immune biomarkers with metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease: a cross-sectional study of NHANES 2007-2018.Front Nutr. 2024 Sep 4;11:1415484. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2024.1415484. eCollection 2024. Front Nutr. 2024. PMID: 39296508 Free PMC article.
-
Effectiveness of Systemic Inflammation Response Index (SIRI) Neutrophil-Lymphocyte Ratio (NLR), Derived Neutrophil-Lymphocyte Ratio (dNLR), and Systemic Immune Inflammation Index (SII) for predicting prognosis of acute diverticulitis.Updates Surg. 2025 May 15. doi: 10.1007/s13304-025-02241-x. Online ahead of print. Updates Surg. 2025. PMID: 40374971
-
The Role of Blood Inflammatory Markers in Salivary Gland Carcinoma: A Scoping Review.J Clin Med. 2025 Mar 6;14(5):1762. doi: 10.3390/jcm14051762. J Clin Med. 2025. PMID: 40095867 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Significance of Simple Inflammatory Markers in Off Pump Surgery-Review.Rev Cardiovasc Med. 2022 Dec 9;23(12):400. doi: 10.31083/j.rcm2312400. eCollection 2022 Dec. Rev Cardiovasc Med. 2022. PMID: 39076673 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Correlation between CBC-derived inflammatory indicators and all-cause mortality with rheumatoid arthritis: a population-based study.Front Med (Lausanne). 2025 Jun 10;12:1538710. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1538710. eCollection 2025. Front Med (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40557044 Free PMC article.
-
Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in type 2 diabetes patients combined with Lower Extremity Peripheral Artery Disease.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Aug 30;15:1434580. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1434580. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39280000 Free PMC article.
-
Predictive role of inflammatory markers in characterizing the progression of interstitial lung disease: a retrospective analysis.Am J Transl Res. 2025 May 15;17(5):3485-3495. doi: 10.62347/JZTW5621. eCollection 2025. Am J Transl Res. 2025. PMID: 40535665 Free PMC article.
-
The diagnostic and prognostic role of novel biomarkers in anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis.Front Immunol. 2025 Jun 17;16:1588287. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1588287. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40599788 Free PMC article.
-
Disease activity in patients with idiopathic inflammatory myopathy according to time since diagnosis and positivity to antisynthetase autoantibodies: data from the Myo-Spain registry.Arthritis Res Ther. 2025 Jan 8;27(1):5. doi: 10.1186/s13075-024-03471-x. Arthritis Res Ther. 2025. PMID: 39780297 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lundberg IA-O, Fujimoto MA-O, Vencovsky JA-O, et al. Idiopathic inflammatory myopathies. Nat Rev Dis Prim. 2021;7(1):86. - PubMed
-
- Loarce-Martos JA-O, Lilleker JA-O, Parker MA-O, McHugh N, Chinoy HA-O. Polymyositis: is there anything left? A retrospective diagnostic review from a tertiary myositis centre. Rheumatology. 2021;60(7):3398–3403. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

