Distinctive tumorigenic significance and innovative oncology targets of SUMOylation
- PMID: 38855173
- PMCID: PMC11155398
- DOI: 10.7150/thno.97162
Distinctive tumorigenic significance and innovative oncology targets of SUMOylation
Abstract
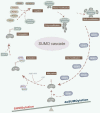
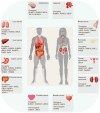
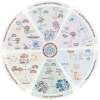
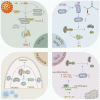
Protein SUMOylation, a post-translational modification, intricately regulates diverse biological processes including gene expression, cell cycle progression, signaling pathway transduction, DNA damage response, and RNA metabolism. This modification contributes to the acquisition of tumorigenicity and the maintenance of cancer hallmarks. In malignancies, protein SUMOylation is triggered by various cellular stresses, promoting tumor initiation and progression. This augmentation is orchestrated through its specific regulatory mechanisms and characteristic biological functions. This review focuses on elucidating the fundamental regulatory mechanisms and pathological functions of the SUMO pathway in tumor pathogenesis and malignant evolution, with particular emphasis on the tumorigenic potential of SUMOylation. Furthermore, we underscore the potential therapeutic benefits of targeting the SUMO pathway, paving the way for innovative anti-tumor strategies by perturbing this dynamic and reversible modifying process.
Keywords: Cancer; Cancer hallmarks; Cancer therapy; Post-translational modification; SUMOylation.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The post-translational modification, SUMOylation, and cancer (Review).Int J Oncol. 2018 Apr;52(4):1081-1094. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2018.4280. Epub 2018 Feb 22. Int J Oncol. 2018. PMID: 29484374 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SUMOylation homeostasis in tumorigenesis.Cancer Lett. 2020 Jan 28;469:301-309. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2019.11.004. Epub 2019 Nov 6. Cancer Lett. 2020. PMID: 31705931 Review.
-
Targeted inhibition of SUMOylation: treatment of tumors.Hum Cell. 2024 Sep;37(5):1347-1354. doi: 10.1007/s13577-024-01092-9. Epub 2024 Jun 10. Hum Cell. 2024. PMID: 38856883 Review.
-
Signalling mechanisms and cellular functions of SUMO.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2022 Nov;23(11):715-731. doi: 10.1038/s41580-022-00500-y. Epub 2022 Jun 24. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2022. PMID: 35750927 Review.
-
Regulation of post-translational modification in breast cancer treatment.BMB Rep. 2019 Feb;52(2):113-118. doi: 10.5483/BMBRep.2019.52.2.017. BMB Rep. 2019. PMID: 30638182 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The impact of dysregulation SUMOylation on prostate cancer.J Transl Med. 2025 Mar 6;23(1):286. doi: 10.1186/s12967-025-06271-2. J Transl Med. 2025. PMID: 40050932 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Deciphering the pseudouridine nucleobase modification in human diseases: From molecular mechanisms to clinical perspectives.Clin Transl Med. 2025 Jan;15(1):e70190. doi: 10.1002/ctm2.70190. Clin Transl Med. 2025. PMID: 39834094 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Mahajan R, Delphin C, Guan T, Gerace L, Melchior F. A small ubiquitin-related polypeptide involved in targeting RanGAP1 to nuclear pore complex protein RanBP2. Cell. 1997;88:97–107. - PubMed
-
- Li B, Kang H, Xiao Y, Du Y, Xiao Y, Song G. et al. LncRNA GAL promotes colorectal cancer liver metastasis through stabilizing GLUT1. Oncogene. 2022;41:1882–94. - PubMed
-
- Liu X, Liu J, Xiao W, Zeng Q, Bo H, Zhu Y. et al. SIRT1 Regulates N(6) -Methyladenosine RNA Modification in Hepatocarcinogenesis by Inducing RANBP2-Dependent FTO SUMOylation. Hepatology. 2020;72:2029–50. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

