A comprehensive review of deep learning in EEG-based emotion recognition: classifications, trends, and practical implications
- PMID: 38855206
- PMCID: PMC11157589
- DOI: 10.7717/peerj-cs.2065
A comprehensive review of deep learning in EEG-based emotion recognition: classifications, trends, and practical implications
Abstract
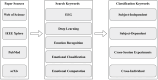
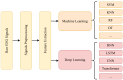
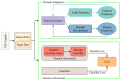
Emotion recognition utilizing EEG signals has emerged as a pivotal component of human-computer interaction. In recent years, with the relentless advancement of deep learning techniques, using deep learning for analyzing EEG signals has assumed a prominent role in emotion recognition. Applying deep learning in the context of EEG-based emotion recognition carries profound practical implications. Although many model approaches and some review articles have scrutinized this domain, they have yet to undergo a comprehensive and precise classification and summarization process. The existing classifications are somewhat coarse, with insufficient attention given to the potential applications within this domain. Therefore, this article systematically classifies recent developments in EEG-based emotion recognition, providing researchers with a lucid understanding of this field's various trajectories and methodologies. Additionally, it elucidates why distinct directions necessitate distinct modeling approaches. In conclusion, this article synthesizes and dissects the practical significance of EEG signals in emotion recognition, emphasizing its promising avenues for future application.
Keywords: Deep learning; Electroencephalogram (EEG); Emotion recognition; Human computer interaction.
©2024 Ma et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare there are no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Deep learning-based EEG emotion recognition: Current trends and future perspectives.Front Psychol. 2023 Feb 27;14:1126994. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2023.1126994. eCollection 2023. Front Psychol. 2023. PMID: 36923142 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Research progress on emotion recognition by combining virtual reality environment and electroencephalogram signals].Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi. 2024 Apr 25;41(2):389-397. doi: 10.7507/1001-5515.202310045. Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi. 2024. PMID: 38686422 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese.
-
EEG-based emotion recognition systems; comprehensive study.Heliyon. 2024 May 18;10(10):e31485. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e31485. eCollection 2024 May 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38818173 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Enhancing the accuracy of electroencephalogram-based emotion recognition through Long Short-Term Memory recurrent deep neural networks.Front Hum Neurosci. 2023 Oct 10;17:1174104. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2023.1174104. eCollection 2023. Front Hum Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37881690 Free PMC article.
-
Emotion recognition in EEG signals using deep learning methods: A review.Comput Biol Med. 2023 Oct;165:107450. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2023.107450. Epub 2023 Sep 9. Comput Biol Med. 2023. PMID: 37708717 Review.
Cited by
-
Application of Graph-Theoretic Methods Using ERP Components and Wavelet Coherence on Emotional and Cognitive EEG Data.Brain Sci. 2025 Jul 2;15(7):714. doi: 10.3390/brainsci15070714. Brain Sci. 2025. PMID: 40722306 Free PMC article.
-
Multi-angle information aggregation for inductive temporal graph embedding.PeerJ Comput Sci. 2024 Nov 26;10:e2560. doi: 10.7717/peerj-cs.2560. eCollection 2024. PeerJ Comput Sci. 2024. PMID: 39650384 Free PMC article.
-
A survey on gait recognition against occlusion: taxonomy, dataset and methodology.PeerJ Comput Sci. 2024 Dec 23;10:e2602. doi: 10.7717/peerj-cs.2602. eCollection 2024. PeerJ Comput Sci. 2024. PMID: 39896378 Free PMC article.
-
Auxiliary classifier adversarial networks with maximum subdomain discrepancy for EEG-based emotion recognition.Med Biol Eng Comput. 2025 Jun 2. doi: 10.1007/s11517-025-03384-0. Online ahead of print. Med Biol Eng Comput. 2025. PMID: 40457127 Review.
-
SensoriMind-Trans Net: EEG and sensorimotor-driven transformer for athlete potential evaluation.Front Psychol. 2025 Apr 28;16:1496013. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2025.1496013. eCollection 2025. Front Psychol. 2025. PMID: 40357467 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aadam TA, Al-Obeidat F, Halim Z, Waqas M, Qayum F. EmoPercept: EEG-based emotion classification through perceiver. Soft Computing. 2022;26:1–8.
-
- Acharya D, Goel S, Bhardwaj H, Sakalle A, Bhardwaj A. A long short term memory deep learning network for the classification of negative emotions using EEG signals. 2020 international joint conference on neural networks (ijcnn); Piscataway. 2020. pp. 1–8.
-
- Adyapady RR, Annappa B. A comprehensive review of facial expression recognition techniques. Multimedia Systems. 2023;29(1):73–103. doi: 10.1007/s00530-022-00984-w. - DOI
-
- Al-Dujaili MJ, Ebrahimi-Moghadam A. Speech emotion recognition: a comprehensive survey. Wireless Personal Communications. 2023;129(4):2525–2561. doi: 10.1007/s11277-023-10244-3. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
