Growth and yield of maize in response to reduced fertilizer application and its impacts on population dynamics and community biodiversity of insects and soil microbes
- PMID: 38855460
- PMCID: PMC11157128
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1362905
Growth and yield of maize in response to reduced fertilizer application and its impacts on population dynamics and community biodiversity of insects and soil microbes
Abstract
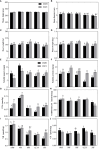
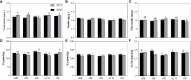
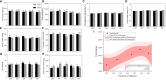
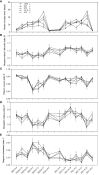
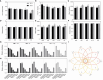
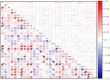
In the North China Plain, farmers are using excessive amounts of fertilizer for the production of high-yield crop yield, which indirectly causes pollution in agricultural production. To investigate an optimal rate of fertilizer application for summer maize, the fertilizer reduction experiments with 600 kg/ha NPK (N: P2O5: K2O = 28: 8: 10) as normal fertilizer application (NFA), (i.e., 100F), were conducted successively during 2020 and 2021 to study the effects of reduced fertilizer rates, including 90% (540 kg/ha; i.e., 90F), 80% (480 kg/ha; i.e., 80F), 62.5% (375 kg/ha; i.e., 62.5F) and 50% (300 kg/ha; i.e., 50F) of NFA, on the plant growth of maize, the dynamics of key population abundances and community diversity of insects, and the composition and diversity of microbial community and finally to find out the N-metabolic enzymes' activity in soil. Our findings revealed that the fertilizer reduction rates by 10% - 20% compared to the current 100% NFA, and it has not significantly affected the plant growth of maize, not only plant growth indexes but also foliar contents of nutrients, secondary metabolites, and N-metabolic enzymes' activity. Further, there was no significant alteration of the key population dynamics of the Asian corn borer (Ostrinia furnacalis) and the community diversity of insects on maize plants. It is interesting to note that the level of N-metabolic enzymes' activity and microbial community diversity in soil were also not affected. While the fertilizer reduction rate by 50% unequivocally reduced field corn yield compared to 100% NFA, significantly decreased the yield by 17.10%. The optimal fertilizer application was calculated as 547 kg/ha (i.e., 91.17% NFA) based on the simulation analysis of maize yields among the five fertilizer application treatments, and the fertilizer application reduced down to 486 kg/ha (i.e., 81.00% NFA) with a significant reduction of maize yield. These results indicated that reduced the fertilizer application by 8.83% - 19.00% is safe and feasible to mitigate pollution and promote sustainable production of maize crops in the region.
Keywords: biomass and yield; fertilizer reduction; insects; maize; soil microbes.
Copyright © 2024 Zou, Li, Wang, Duan, Dong, Zhang, Du and Chen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Impacts of corn intercropping with soybean, peanut and millet through different planting patterns on population dynamics and community diversity of insects under fertilizer reduction.Front Plant Sci. 2022 Oct 18;13:936039. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.936039. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 36330264 Free PMC article.
-
Variation in yield gap induced by nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium fertilizer in North China Plain.PLoS One. 2013 Dec 12;8(12):e82147. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0082147. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24349204 Free PMC article.
-
[Effects of Controlled-release Blended Fertilizer on Crop Yield and Greenhouse Gas Emissions in Wheat-maize Rotation System].Huan Jing Ke Xue. 2024 May 8;45(5):2891-2904. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.202305191. Huan Jing Ke Xue. 2024. PMID: 38629551 Chinese.
-
Sole and Combined Application of Biodigestate, N, P, and K Fertilizers: Impacts on Soil Chemical Properties and Maize Performance.ScientificWorldJournal. 2024 Feb 20;2024:6685906. doi: 10.1155/2024/6685906. eCollection 2024. ScientificWorldJournal. 2024. PMID: 38414494 Free PMC article.
-
Developing recommendations for increased productivity in cassava-maize intercropping systems in Southern Nigeria.Field Crops Res. 2021 Oct 1;272:108283. doi: 10.1016/j.fcr.2021.108283. Field Crops Res. 2021. PMID: 34840408 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Early warning of Aspergillus contamination in maize by gas chromatography-ion mobility spectrometry.Front Microbiol. 2024 Sep 26;15:1470115. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1470115. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39391609 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

