The evaluation of human endogenous retroviral env expression in normal and cancerous tissues of the breast
- PMID: 38855560
- PMCID: PMC11162086
- DOI: 10.4103/jrms.jrms_141_23
The evaluation of human endogenous retroviral env expression in normal and cancerous tissues of the breast
Abstract
Background: Both internal and external risk factors can accelerate the progression of breast cancer which is the reason why clinicians have tried to find new biomarkers for this health problem. Human endogenous retrovirus-W (HERV-W) can be one of these biomarkers, as it has been mentioned that some genes of this virus are able to have either higher or lower expression in numerous cancerous cells. In this study, we aimed to compare HERV-W envelope expression in breast cancer tissues and normal ones since its effects on this malignancy have not been clear.
Materials and methods: We collected 46 breast cancer tissues and their normal adjacent ones. After extracting the RNA of breast samples, we evaluated the expression of HERV-W envelope syncytin-1 and 2 using quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR) in different kinds of breast cancer stages.
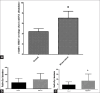
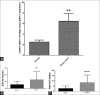
Results: Data showed that more than 13% of patients had a family history of breast cancer; moreover, approximately half of the tissues were estrogen receptor or progesterone receptor positive. Lymph node metastasis was seen in 52% of the patients, and about 40% of tumors were larger than 2 cm. Real-time PCR showed that syncytin-1 and 2 had upward regulation with (*P < 0.05) and (**P < 0.01), respectively.
Conclusion: As the expression of HERV-W Env (syncytin-1, syncytin-2) was higher in breast cancerous tissues in comparison with normal ones, we believe that these genes may have a role to play in monitoring patients suffering from this type of cancer. However, further studies are needed to confirm this hypothesis.
Keywords: Breast; cancer; syncytin- 2; syncytin-1.
Copyright: © 2024 Journal of Research in Medical Sciences.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Role of HERV-W syncytin-1 in placentation and maintenance of human pregnancy.Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol. 2009 Jul;17(4):319-28. doi: 10.1097/PAI.0b013e31819640f9. Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol. 2009. PMID: 19407656
-
Expression of human endogenous retrovirus-w including syncytin-1 in cutaneous T-cell lymphoma.PLoS One. 2013 Oct 1;8(10):e76281. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0076281. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24098463 Free PMC article.
-
The important biological roles of Syncytin-1 of human endogenous retrovirus W (HERV-W) and Syncytin-2 of HERV-FRD in the human placenta development.Mol Biol Rep. 2023 Sep;50(9):7901-7907. doi: 10.1007/s11033-023-08658-0. Epub 2023 Jul 8. Mol Biol Rep. 2023. PMID: 37421503 Review.
-
Expression of Human Endogenous Retrovirus Type K Envelope Protein is a Novel Candidate Prognostic Marker for Human Breast Cancer.Genes Cancer. 2011 Sep;2(9):914-22. doi: 10.1177/1947601911431841. Genes Cancer. 2011. PMID: 22593804 Free PMC article.
-
Human Endogenous Retroviral Envelope Protein Syncytin-1 and Inflammatory Abnormalities in Neuropsychological Diseases.Front Psychiatry. 2018 Sep 7;9:422. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2018.00422. eCollection 2018. Front Psychiatry. 2018. PMID: 30245643 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- DeSantis CE, Fedewa SA, Goding Sauer A, Kramer JL, Smith RA, Jemal A. Breast cancer statistics, 2015:Convergence of incidence rates between black and white women. CA Cancer J Clin. 2016;66:31–42. - PubMed
-
- Dadashi M, Eslami G, Faghihloo E, Pourmohammad A, Hosseini J, Taheripanah R, et al. Detection of human papilloma virus type 16 in epithelial ovarian tumors samples. Arch Clin Infect Dis. 2017;12:e39666.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
