A detailed overview of quercetin: implications for cell death and liver fibrosis mechanisms
- PMID: 38855739
- PMCID: PMC11157233
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1389179
A detailed overview of quercetin: implications for cell death and liver fibrosis mechanisms
Abstract
Background: Quercetin, a widespread polyphenolic flavonoid, is known for its extensive health benefits and is commonly found in the plant kingdom. The natural occurrence and extraction methods of quercetin are crucial due to its bioactive potential.
Purpose: This review aims to comprehensively cover the natural sources of quercetin, its extraction methods, bioavailability, pharmacokinetics, and its role in various cell death pathways and liver fibrosis.
Methods: A comprehensive literature search was performed across several electronic databases, including PubMed, Embase, CNKI, Wanfang database, and ClinicalTrials.gov, up to 10 February 2024. The search terms employed were "quercetin", "natural sources of quercetin", "quercetin extraction methods", "bioavailability of quercetin", "pharmacokinetics of quercetin", "cell death pathways", "apoptosis", "autophagy", "pyroptosis", "necroptosis", "ferroptosis", "cuproptosis", "liver fibrosis", and "hepatic stellate cells". These keywords were interconnected using AND/OR as necessary. The search focused on studies that detailed the bioavailability and pharmacokinetics of quercetin, its role in different cell death pathways, and its effects on liver fibrosis.
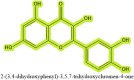
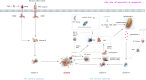
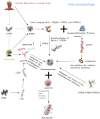
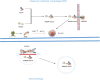
Results: This review details quercetin's involvement in various cell death pathways, including apoptosis, autophagy, pyroptosis, necroptosis, ferroptosis, and cuproptosis, with particular attention to its regulatory influence on apoptosis and autophagy. It dissects the mechanisms through which quercetin affects these pathways across different cell types and dosages. Moreover, the paper delves into quercetin's effects on liver fibrosis, its interactions with hepatic stellate cells, and its modulation of pertinent signaling cascades. Additionally, it articulates from a physical organic chemistry standpoint the uniqueness of quercetin's structure and its potential for specific actions in the liver.
Conclusion: The paper provides a detailed analysis of quercetin, suggesting its significant role in modulating cell death mechanisms and mitigating liver fibrosis, underscoring its therapeutic potential.
Keywords: apoptosis; autophagy; cuproptosis; ferroptosis; liver fibrosis; necroptosis; pyroptosis; quercetin.
Copyright © 2024 Xiong, Zhang, Li, Tang, Song, Zhou and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Selected Flavonols Targeting Cell Death Pathways in Cancer Therapy: The Latest Achievements in Research on Apoptosis, Autophagy, Necroptosis, Pyroptosis, Ferroptosis, and Cuproptosis.Nutrients. 2024 Apr 18;16(8):1201. doi: 10.3390/nu16081201. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 38674891 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A review on anti-cancer properties of quercetin in gastric cancer.Front Pharmacol. 2025 May 19;16:1563229. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1563229. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40458787 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Quercetin's Effects on Glutamate Cytotoxicity.Molecules. 2022 Nov 7;27(21):7620. doi: 10.3390/molecules27217620. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36364448 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anti-Inflammatory and Anti-Arthritis Activity of Quercetin: A Comprehensive Review.Curr Rheumatol Rev. 2025;21(2):144-159. doi: 10.2174/0115733971280645240415101912. Curr Rheumatol Rev. 2025. PMID: 38808723 Review.
-
Targeting cell death pathways for cancer therapy: recent developments in necroptosis, pyroptosis, ferroptosis, and cuproptosis research.J Hematol Oncol. 2022 Dec 8;15(1):174. doi: 10.1186/s13045-022-01392-3. J Hematol Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36482419 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Hepatocytes as Model for Investigating Natural Senotherapeutic Compounds and Their Effects on Cell Cycle Dynamics and Genome Stability.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jul 16;26(14):6794. doi: 10.3390/ijms26146794. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40725041 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Isorhamnetin: Reviewing Recent Developments in Anticancer Mechanisms and Nanoformulation-Driven Delivery.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jul 30;26(15):7381. doi: 10.3390/ijms26157381. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40806510 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Unlocking the potential of pyroptosis in tumor immunotherapy: a new horizon in cancer treatment.Front Immunol. 2024 Jun 14;15:1381778. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1381778. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38947336 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Systematic Review: Quercetin-Secondary Metabolite of the Flavonol Class, with Multiple Health Benefits and Low Bioavailability.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Nov 11;25(22):12091. doi: 10.3390/ijms252212091. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39596162 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

