Proteins linking APOE ɛ4 with Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 38856164
- PMCID: PMC11247662
- DOI: 10.1002/alz.13867
Proteins linking APOE ɛ4 with Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
Introduction: The ɛ4 allele of the apolipoprotein E gene (APOE ɛ4) is the strongest genetic risk factor for Alzheimer's disease (AD), but the mechanisms connecting APOE ɛ4 to AD are not clear.
Methods: Participants (n = 596) were from two clinical-pathological studies. Tissues from dorsolateral prefrontal cortex were examined to identify 8425 proteins. Post mortem pathological assessment used immunohistochemistry to obtain amyloid beta (Aβ) load and tau tangle density.
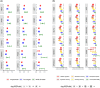
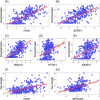
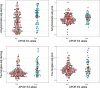
Results: In separate models, APOE ɛ4 was associated with 18 proteins, which were associated with Aβ and tau tangles. Examining the proteins in a single model identified Netrin-1 and secreted frizzled-related protein 1 (SFRP1) as the two proteins linking APOE ɛ4 with Aβ with the largest effect sizes and Netrin-1 and testican-3 linking APOE ɛ4 with tau tangles.
Discussion: We identified Netrin-1, SFRP1, and testican-3 as the most promising proteins that link APOE ɛ4 with Aβ and tau tangles.
Highlights: Of 8425 proteins extracted from prefrontal cortex, 18 were related to APOE ɛ4. The 18 proteins were also related to amyloid beta (Aβ) and tau. The 18 proteins were more related to APOE ɛ4 than other AD genetic risk variants. Netrin-1 and secreted frizzled-related protein 1 were the two most promising proteins linking APOE ɛ4 with Aβ. Netrin-1 and testican-3 were two most promising proteins linking APOE ɛ4 with tau.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease; amyloid; apolipoprotein ε4; proteins; tau proteins.
© 2024 The Author(s). Alzheimer's & Dementia published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of Alzheimer's Association.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no disclosures relevant to the manuscript. Author disclosures are available in the supporting information.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Association of Apolipoprotein E ε4 With Transactive Response DNA-Binding Protein 43.JAMA Neurol. 2018 Nov 1;75(11):1347-1354. doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2018.3139. JAMA Neurol. 2018. PMID: 30422173 Free PMC article.
-
[Expression of apolipoprotein E in Alzheimer's disease and its significance].Zhonghua Bing Li Xue Za Zhi. 2005 Sep;34(9):556-60. Zhonghua Bing Li Xue Za Zhi. 2005. PMID: 16468304 Chinese.
-
Profiles of β-Amyloid Peptides and Key Secretases in Brain Autopsy Samples Differ with Sex and APOE ε4 Status: Impact for Risk and Progression of Alzheimer Disease.Neuroscience. 2018 Mar 1;373:20-36. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2018.01.005. Epub 2018 Jan 11. Neuroscience. 2018. PMID: 29331531
-
Cellular cholesterol homeostasis and Alzheimer's disease.J Lipid Res. 2017 Dec;58(12):2239-2254. doi: 10.1194/jlr.R075630. Epub 2017 Mar 15. J Lipid Res. 2017. PMID: 28298292 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The effect of apolipoprotein E (ApoE) genotype on biomarkers of amyloidogenesis, tau pathology and neurodegeneration in Alzheimer's disease.Clin Chem Lab Med. 2011 Mar;49(3):375-83. doi: 10.1515/CCLM.2011.088. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2011. PMID: 21388338 Review.
Cited by
-
Proteomic signatures of the APOE ε4 and APOE ε2 genetic variants and Alzheimer's disease.medRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Aug 25:2025.08.04.25332945. doi: 10.1101/2025.08.04.25332945. medRxiv. 2025. PMID: 40799961 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Brain Region-specific Accumulation of Amyloidosis-associated Proteins in Postmortem Brain Tissues of Alzheimer's Disease Patients.Res Sq [Preprint]. 2025 Jun 3:rs.3.rs-6649354. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-6649354/v1. Res Sq. 2025. Update in: Mol Neurobiol. 2025 Jul 24. doi: 10.1007/s12035-025-05231-7. PMID: 40502767 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Brain Region-Specific Accumulation of Amyloidosis-Associated Proteins in Postmortem Brain Tissues of Alzheimer's Disease Patients.Mol Neurobiol. 2025 Jul 24. doi: 10.1007/s12035-025-05231-7. Online ahead of print. Mol Neurobiol. 2025. PMID: 40705253
-
Profiling 92 circulating neurobiological proteins identifies novel candidate biomarkers of long-term cognitive outcome after ischemic stroke.Sci Rep. 2025 May 2;15(1):15328. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-99735-w. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40316737 Free PMC article.
-
Trends and challenges of AAV-delivered gene editing therapeutics for CNS disorders: Implications for neurodegenerative disease.Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2025 Jul 17;36(3):102635. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2025.102635. eCollection 2025 Sep 9. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2025. PMID: 40799507 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Farrer LA, Cupples LA, Haines JL, et al. Effects of age, sex, and ethnicity on the association between apolipoprotein E genotype and Alzheimer disease. A meta‐analysis. APOE and Alzheimer Disease Meta Analysis Consortium. JAMA. 1997;278:1349‐1356. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

