Conservative interdisciplinary management for a congenitally missing maxillary lateral incisor in an adolescent patient
- PMID: 38856304
- PMCID: PMC11845843
- DOI: 10.1111/adj.13027
Conservative interdisciplinary management for a congenitally missing maxillary lateral incisor in an adolescent patient
Abstract
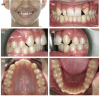
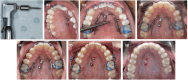
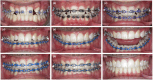
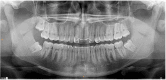
A congenitally missing lateral incisor tooth is commonly associated with both short and long-term clinical dilemmas, particularly for a growing patient. A unilaterally missing maxillary lateral incisor tooth creates a significant dental asymmetry in the critical aesthetic zone of the smile and potentially increases the difficulty of any subsequent orthodontic and restorative treatment. Carefully planned interdisciplinary management is required to address the challenges of anterior dental asymmetry, unilateral orthodontic space closure and to alleviate the concerns that accompany restorative implant placement in the anterior maxilla. The use of skeletal temporary anchorage devices has increased the predictability of orthodontic space closure, particularly for missing maxillary lateral incisor cases which were previously considered to be unsuitable.
Keywords: Interdisciplinary management; adolescent patient; congenitally missing maxillary lateral incisor; critical aesthetic zone; temporary anchorage devices.
© 2024 The Author(s). Australian Dental Journal published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of Australian Dental Association.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Prosthetic replacement vs space closure for maxillary lateral incisor agenesis: A systematic review.Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2016 Aug;150(2):228-37. doi: 10.1016/j.ajodo.2016.01.018. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2016. PMID: 27476355
-
Unilateral Agenesis of the Upper Permanent Lateral Incisors in Growing Patients: Gap Closure or Gap Opening? A Systematic Review.Int Dent J. 2025 Aug;75(4):100815. doi: 10.1016/j.identj.2025.03.024. Epub 2025 Jul 3. Int Dent J. 2025. PMID: 40614296 Free PMC article.
-
Retrospective Radiographic Analysis and Treatment Outcomes of Patients With Congenitally Missing Maxillary Lateral Incisors.J Oral Implantol. 2025 Jul 15;51(3):283-288. doi: 10.1563/aaid-joi-D-24-00185. J Oral Implantol. 2025. PMID: 40106832
-
Treatment options for congenitally missing lateral incisors.Eur J Oral Implantol. 2016;9 Suppl 1:S5-24. Eur J Oral Implantol. 2016. PMID: 27314109
-
Invisible treatment with preadjusted lingual appliance and monolateral space opening for an adult Class II malocclusion with upper lateral incisors agenesis: An ortho-prosthetic case report.Int Orthod. 2025 Mar;23(1):100937. doi: 10.1016/j.ortho.2024.100937. Epub 2024 Oct 29. Int Orthod. 2025. PMID: 39471642
References
-
- Khalaf K, Miskelly J, Voge E, Macfarlane TV. Prevalence of hypodontia and associated factors: a systematic review and meta‐analysis. J Orthod 2014;41(4):299–316. - PubMed
-
- Krassnig M, Fickl S. Congenitally missing lateral incisors – a comparison between restorative, implant, and orthodontic approaches. Dent Clin N Am 2011;55(2):283–299. viii. - PubMed
-
- Nunn JH, Carter NE, Gillgrass TJ, et al. The interdisciplinary management of hypodontia: background and role of paediatric dentistry. Br Dent J 2003;194(5):245–251. - PubMed
-
- Westgate E, Waring D, Malik O, Darcey J. Management of missing maxillary lateral incisors in general practice: space opening versus space closure. Br Dent J 2019;226(6):400–406. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

