Streptococcus dysgalactiae subsp. equisimilis infection and its intersection with Streptococcus pyogenes
- PMID: 38856686
- PMCID: PMC11392527
- DOI: 10.1128/cmr.00175-23
Streptococcus dysgalactiae subsp. equisimilis infection and its intersection with Streptococcus pyogenes
Abstract
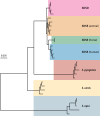
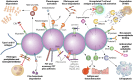
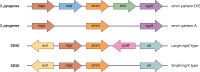
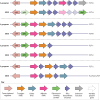
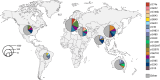
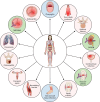
SUMMARYStreptococcus dysgalactiae subsp. equisimilis (SDSE) is an increasingly recognized cause of disease in humans. Disease manifestations range from non-invasive superficial skin and soft tissue infections to life-threatening streptococcal toxic shock syndrome and necrotizing fasciitis. Invasive disease is usually associated with co-morbidities, immunosuppression, and advancing age. The crude incidence of invasive disease approaches that of the closely related pathogen, Streptococcus pyogenes. Genomic epidemiology using whole-genome sequencing has revealed important insights into global SDSE population dynamics including emerging lineages and spread of anti-microbial resistance. It has also complemented observations of overlapping pathobiology between SDSE and S. pyogenes, including shared virulence factors and mobile gene content, potentially underlying shared pathogen phenotypes. This review provides an overview of the clinical and genomic epidemiology, disease manifestations, treatment, and virulence determinants of human infections with SDSE with a particular focus on its overlap with S. pyogenes. In doing so, we highlight the importance of understanding the overlap of SDSE and S. pyogenes to inform surveillance and disease control strategies.
Keywords: Streptococcus; Streptococcus dysgalactiae; Streptococcus pyogenes; group C/G Streptococcus.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Davies MR, McMillan DJ, Beiko RG, Barroso V, Geffers R, Sriprakash KS, Chhatwal GS. 2007. Virulence profiling of Streptococcus dysgalactiae subspecies equisimilis isolated from infected humans reveals 2 distinct genetic lineages that do not segregate with their phenotypes or propensity to cause diseases. Clin Infect Dis 44:1442–1454. doi: 10.1086/516780 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

