Mis-splicing of Mitotic Regulators Sensitizes SF3B1-Mutated Human HSCs to CHK1 Inhibition
- PMID: 38856693
- PMCID: PMC11369594
- DOI: 10.1158/2643-3230.BCD-23-0230
Mis-splicing of Mitotic Regulators Sensitizes SF3B1-Mutated Human HSCs to CHK1 Inhibition
Abstract
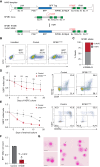
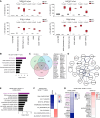
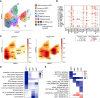
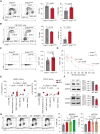
Splicing factor SF3B1 mutations are frequent somatic lesions in myeloid neoplasms that transform hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) by inducing mis-splicing of target genes. However, the molecular and functional consequences of SF3B1 mutations in human HSCs and progenitors (HSPCs) remain unclear. Here, we identify the mis-splicing program in human HSPCs as a targetable vulnerability by precise gene editing of SF3B1 K700E mutations in primary CD34+ cells. Mutant SF3B1 induced pervasive mis-splicing and reduced expression of genes regulating mitosis and genome maintenance leading to altered differentiation, delayed G2/M progression, and profound sensitivity to CHK1 inhibition (CHK1i). Mis-splicing or reduced expression of mitotic regulators BUBR1 and CDC27 delayed G2/M transit and promoted CHK1i sensitivity. Clinical CHK1i prexasertib selectively targeted SF3B1-mutant immunophenotypic HSCs and abrogated engraftment in vivo. These findings identify mis-splicing of mitotic regulators in SF3B1-mutant HSPCs as a targetable vulnerability engaged by pharmacological CHK1 inhibition. Significance: In this study, we engineer precise SF3B1 mutations in human HSPCs and identify CHK1 inhibition as a selective vulnerability promoted by mis-splicing of mitotic regulators. These findings uncover the mis-splicing program induced by mutant SF3B1 in human HSPCs and show that it can be therapeutically targeted by clinical CHK1 inhibitors.
©2024 The Authors; Published by the American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr. Bradley reports grants, personal fees, and other support from Codify Therapeutics and other support from Synthesize Bio outside the submitted work.
Figures

References
-
- Bernard E, Tuechler H, Greenberg PL, Hasserjian RP, Ossa JEA, Nannya Y, et al. . Molecular international prognostic scoring system for myelodysplastic syndromes. NEJM Evid 2022;1:1–14. - PubMed
-
- Darman RB, Seiler M, Agrawal A, Lim KH, Peng S, Aird D, et al. . Cancer-associated SF3B1 hotspot mutations induce cryptic 3’ splice site selection through use of a different branch point. Cell Rep 2015;13:1033–45. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- RC2 DK127989/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL169156/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- DP2 HL147126/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 20125/Associazione Italiana per la Ricerca sul Cancro
- P30CA015704/National Cancer Institute (NCI)
- R01 HL128239/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01HL128239/National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI)
- R01 CA251138/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- DP2HL147126/Common Fund (NIH Common Fund)
- R01CA251138/National Cancer Institute (NCI)
- Mark Foundation For Cancer Research (The Mark Foundation for Cancer Research)
- C355/A26819/Cancer Research UK (CRUK)
- 28390/AIRC Postdoctoral Fellowship
- Scholar Award 1391-24/Leukemia and Lymphoma Society (LLS)
- P30 CA015704/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- Discovery Research Grant/Edward P. Evans Foundation
- R01HL151651/National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI)
- Discovery Grant/Kuni Foundation
- Damon Runyon Cancer Research Foundation (DRCRF)
- RC2DK127989/National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK)
- R01 HL151651/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- Blood Cancer Discoveries Grant/Leukemia and Lymphoma Society (LLS)
- R01HL169156/National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

