Race-Related Differences in Sipuleucel-T Response among Men with Metastatic Castrate-Resistant Prostate Cancer
- PMID: 38856749
- PMCID: PMC11240276
- DOI: 10.1158/2767-9764.CRC-24-0112
Race-Related Differences in Sipuleucel-T Response among Men with Metastatic Castrate-Resistant Prostate Cancer
Abstract
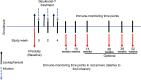
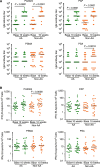
Sipuleucel-T is an autologous cellular immunotherapy that targets prostatic acid phosphatase (PAP) and is available for treatment of men with asymptomatic or minimally symptomatic metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC). In this single-arm, two-cohort, multicenter clinical study, potential racial differences in immune responses to sipuleucel-T in men with mCRPC were explored. Patients' blood samples were obtained to assess serum cytokines, humoral responses, and cellular immunity markers before and after treatment. Baseline cumulative product parameters (total nucleated and CD54+ cell counts and CD54 upregulation) were evaluated. IgM titers against the immunogen PA2024, the target antigen PAP, prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA) and prostate-specific antigen (PSA) were quantified by ELISA. Cytotoxic T-lymphocyte activity was determined by ELISpots, and cytokine and chemokine concentrations were determined by Luminex.Twenty-nine African American (AA) men and 28 non-African American (non-AA) men with mCRPC received sipuleucel-T. Baseline total nucleated cell count, CD54+ cell count, CD54 expression, and cumulative product parameters were higher in non-AA men. Although PSA baseline levels were higher in AA men, there were no racial differences in IgM antibody and IFNγ ELISpots responses against PA2024, PAP, PSA, and PSMA before and after treatment. Expression of co-stimulatory receptor ICOS on CD4+ and CD8+ T cells, and the levels of Th1 cytokine granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor and chemokines CCL4 and CCL5, were significantly higher in AA men before and/or after treatment. Despite no difference in the overall survival, PSA changes from baseline were significantly different between the two races. The data suggest that immune correlates in blood differ in AA and non-AA men with mCRPC pre- and post-sipuleucel-T.
Significance: Our novel findings of higher expression of co-stimulatory receptor ICOS on CD4+ and CD8+ T cells in African American patients with metastatic castrate-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC) prior and post-sipuleucel-T suggest activation of CD4+ and CD8+ T cells. The data indicate that racial differences observed in these and other immune correlates before and after sipuleucel-T warrant additional investigation to further our understanding of the immune system in African American men and other men with mCRPC.
©2024 The Authors; Published by the American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors have completed and submitted the ICMJE Form for Disclosure of Potential Conflicts of Interest. E.I. Heath reports other from Astellas, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Sanofi, Janssen, Caris, Seattle Genetics, Arvinas, BioXcel, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Calibr, Calithera, Corcept, Corvis, Daiichi Sankyo, Eisai, Exelixis, Five Prime, Fortis, GlaxoSmithKline, Gilead Sciences, Harpoon, Hoffman-La Roche, Infinity, iTeos, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Merck, Mirati, Modra, Novartis, Oncolys, Peloton, Pfizer, Pharmacyclics, and POINT Biopharma outside the submitted work. C. Hwang reports grants from Dendreon during the conduct of the study; grants from Merck, AstraZeneca, Seagen/Seattle Genetics, Taiho Oncology, Hengrui, Bayer, Scholar Rock, Exelixis, Century Therapeutics, FUJIFILM Pharmaceuticals, and Shionogi, personal fees from EMD Sorono, TEMPUS, Janssen, Genzyme, and Astellas, and other from Johnson and Johnson outside the submitted work. U.N. Vaishampayan reports grants and personal fees from Merck and BMS; personal fees from Bayer, Pfizer, Gilead, Exelixis, Aveo, Alkermes, and Janssen outside the submitted work. L.G. Lum reports grants from Dendreon, NIH Cancer Support Grant, and other from University of Virginia during the conduct of the study; other from Transtarget, Inc., personal fees from Rapa Therapeutics, and personal fees and other from Tundra Targeted Therapeutics outside the submitted work. No other disclosures were reported.
Figures



References
-
- FDA Approves Provenge. [cited 2024 Feb 08]. Available from:https://www.drugs.com/newdrugs/fda-approves-provenge-cellular-immunother....
-
- Cheever MA, Higano CS. PROVENGE (sipuleucel-T) in prostate cancer: the first FDA-approved therapeutic cancer vaccine. Clin Cancer Res 2011;17:3520–6. - PubMed
-
- Sipuleucel-T: APC 8015, APC-8015, prostate cancer vaccine-Dendreon. Drugs R D 2006;7:197–201. - PubMed
-
- Kantoff PW, Higano CS, Shore ND, Berger ER, Small EJ, Penson DF, et al. ; IMPACT Study Investigators . Sipuleucel-T immunotherapy for castration-resistant prostate cancer. N Engl J Med 2010;363:411–22. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

